| Multiple Representations is the idea that a physical phenomena can be explored in many different ways. For example, there is the physical representation which models the system with figures and diagrams, such as a free body diagram. There is also the mathematical representation which uses the equation(s) governing the physics of the system. All of the representations can be used together to help us understand and quantify the physical phenomena. |
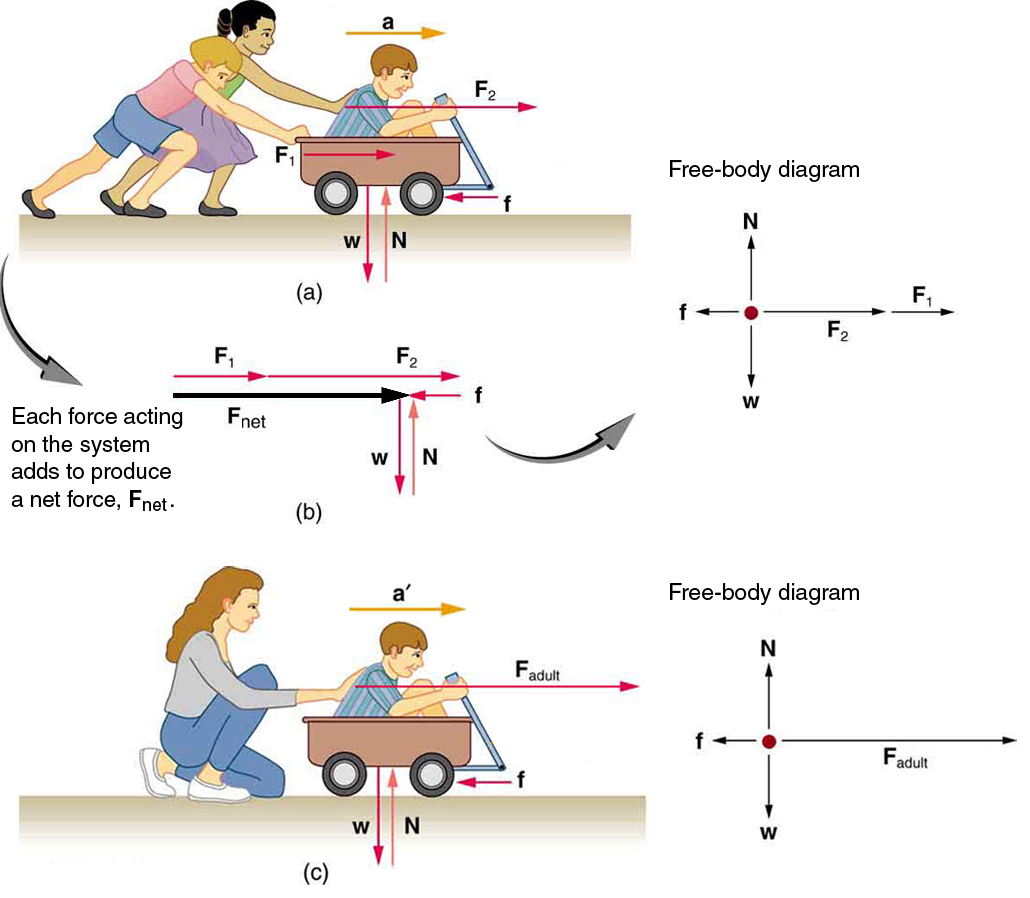
The mathematics involved with free body diagrams are in the translation to Newton's Second Law.
The free body diagrams are tools to help set up Newton's second law, check out the Second law graphical representation section for a better perspective.
Presentation of FBD that includes the introduction of the normal force, tension, and universal gravitation, restoring force
Animation that differentiates between forces acting on a box in the back of a truck and the forces acting the truck
Video Series with an introduction to FBD's and multiple examples.
