| # | Title | Image | Description | Video |
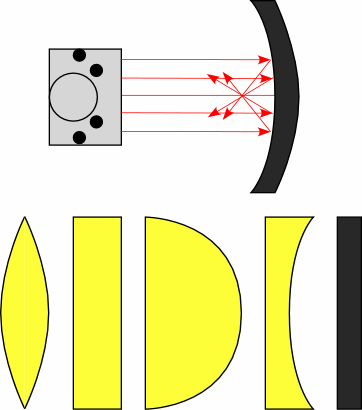
| 1 | Concave and Convex Mirrors |
Reflection from Curved Surfaces
|
Shine parallel beams at convex and concave mirrors. |
Video 2 |
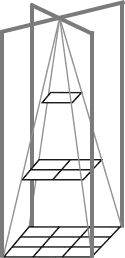
| 2 | Inverse Square Model |
Luminosity
|
Place pointed end next to a light source. As the light crosses the first plane, we see a square area that is equal to one unit of light. At the next level we notice that the same amount of light now covers four times the area. Therefore, it is 1/4 as bright per unit area as the first level. At the bottom level, we notice it covers nine times the area or it is 1/9 as bright. |
Video 2 |
| 1 | Projected Filament w/Lens |
Thin Lenses
|
Turn on the light bulb. Move the light bulb to focus the image on the side wall. The focal lengths are marked on the lenses. Show the effect of aperture size on the sharpness on the focus by placing different sized stops in front of the lens. |
Video 2 |
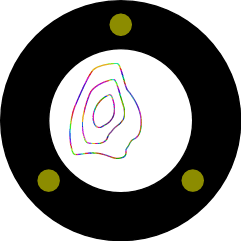
| 2 | Newton's Rings |
Thin Films
|
Turn on the light. The interference pattern is projected onto the side wall. Change the pattern by tightening a screw on the edge of the glass disk. |
Video 2 |
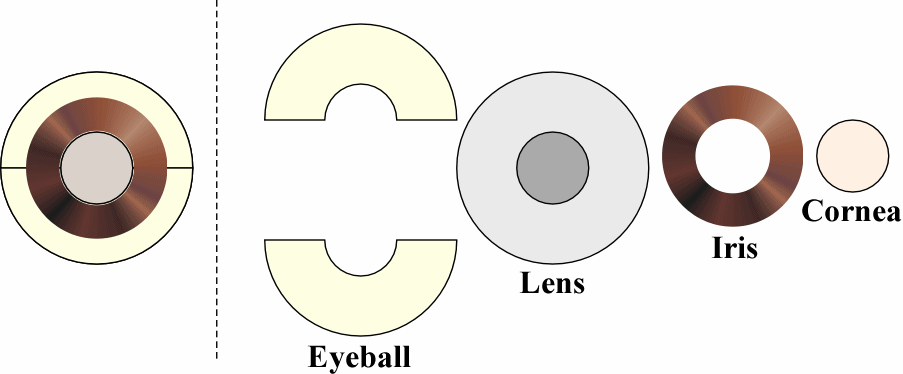
| 3 | Eye Model |
The Eye
|
The standard take-apart eye model. |