K-2D-1 The velocity of a cheetah is found to be <15, -10> m/s. What is the speed and direction of the cheetah's motion? Assume a standard x and y coordinate system.
1. 18 m/s, 33.7º from +x towards -y
2. 9 m/s, 44.4º from +x towards -y
3. 21 m/s, 12.0º from -x towards +y
4. 13.5 m/s, 33.3º from -x towards –y
5. 17.1 m/s, 58.7º from x towards y
K-2D-2 Upon waking from being hit in the head with a shovel you find yourself in the woods, next to a unfilled grave. You start running from this nightmare in a direction 51.34 degree from the negative y direction towards the negative x direction. Your acute direction senses surprise you but this is no time to contemplate a new super-power. You run along that line for 6.403 miles until you run into a police officer located at a location <-2, -3> miles from the police station. What are the coordinates of the grave you were presumably destined for?
1. <1, 8> mi
2. <4, -5> mi
3. <-2, 3> mi
4. <-1, -1> mi
5. <3, 1> mi
K-2D-3 An object starts at the initial position indicated below. It travels with the average velocity represented below for 3 s. Sketch on the plot below the final position of the object.
Assume the grid spacing is 1 m for position vectors and 1 m/s for velocity vectors.
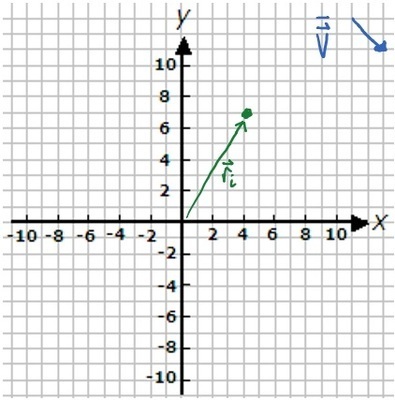
What is the final position vector of the object?
1. <-2, 12> m
2. -<10, 1> m
3. -<-10, -1> m
4. <4, -10> m
5. <10, -1> m
6. <10, 13> m
K-2D-4 A spaceship is traveling in the galactic northeast direction. The ship's thrusters then create a large constant acceleration in the southern direction. Which of the following statements are necessarily true regarding the time after the thrusters have fired.
1. The ship will be moving in the southeast direction.
2. The ship will eventually be moving in the southern direction
3. The ship's displacement will be in the southern direction
4. The ship will eventually be moving with both southern and eastern components
5. The change in the ship's velocity will be in the southern direction.
K-2D-5 The change in position vector for an African Swallow you are studying is determined to be in a direction 36.87º from +x towards +y. The x-component is 40 m. What is the magnitude of the displacement in meters?
K-2D-6 Deserted on a deserted Island you spot a slightly exposed tin can under a tree. Upon opening it you find instructions to a buried treasure. It reads: “Ten paces from this very tree in a direction twenty degrees south of west lies the first location. Ten paces from this very tree in a direction sixty degrees north of east lies the second location. Walk from this tree exactly the distance and direction you would walk from the first location to the second location and you will find ye treasure. Yar” Sketch a physical representation of this situation on the grid provided. A physical representation for this type of problem should include the two position vectors, the change in the position vector, and the location of the treasure. Use the center of the grid as the tree location and scale appropriately to fit on the grid.
What are the coordinates of treasure?
K-2D-7a Estimate the position vector to the location in the room defined as point A. Set the origin at the front, bottom, right side of the room (as seen by the students). Consider left to right as the positive x direction, bottom to top as positive y direction, and front to back as the positive z direction.
Answer in whole numbers of meters with the following format: <x,y,z> m. An example might look like: <4,1,7> m.
Estimate the position vector to the location in the room defined as point B.
Using the class average for position vectors A and B, find the displacement vector from point A to B. Answer in whole numbers of meters with the following format: <Δx,Δy,Δz>. An example might look like: <4,1,7> m.
K-2D-7b New Origin
Estimate the position vector to the locations in the room defined as point A and point B.
This time set the origin at the front, top, left side of the room (as seen by the students). Consider left to right as the positive x direction, bottom to top as positive y direction, and front to back as the positive z direction.
Answer in whole numbers of meters with the following format: <xA,yA,zA> m, <xB,yB,zB> m. An example might look like: <4,1,7> m, <-2,3,6> m.
Using the class average for position vectors A and B from the new origin, find the displacement vector from point A to B.
Answer in whole numbers of meters with the following format: <Δx,Δy,Δz>. An example might look like: <4,1,7> m.
K-2D-8 You take off from La Guardia airport in a little airplane. First you fly NW for 5 miles. At the George Washington bridge, you turn SSW for 10 miles. Above the Statue of Liberty, you turn S toward the Verazzano Narrows bridge, 5 miles ahead. Over the bridge you turn ENE for a landing at JFK airport, 10 miles ahead.
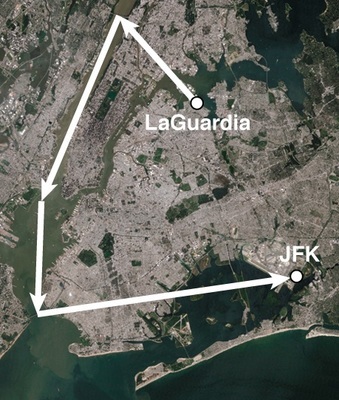
Suppose that instead of flying NW-SSW-S-ENE, you had followed the same "vectors" in a different sequence: SSW-NW-ENE-S. Mark on the map where this path would have led you.
K-2D-9 Upon waking from being hit in the head with a shovel you find yourself in the woods, next to a unfilled grave. You start running from this nightmare in a direction 51.34 degree from the negative y direction towards the negative x direction. Your acute direction senses surprise you but this is no time to contemplate a new super-power. You run along that line for 6.403 miles until you run into a police officer located at a location <-2, -3> miles from the police station. What are the coordinates of the grave you were presumably destined for?
1. <1, 8> mi
2. <4, -5> mi
3. <-2, 3> mi
4. <-1, -1> mi
5. <3, 1> mi
K-2D-10 An object has a final position as indicated below. It traveled with the average velocity represented below for 4 s. Sketch on the plot below the initial position of the object.
Assume the grid spacing is 1 m for position vectors and 1 m/s for velocity vectors.
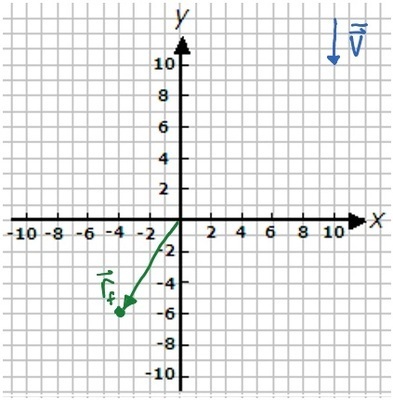
K-2D-11 If the time between the initial and the final velocity data points being acquired is 2 s, sketch on the vector operation plot below the average acceleration vector.
Note: Assume the grid spacing is 1 m/s for velocity vectors and 1 m/s2 for acceleration vectors.
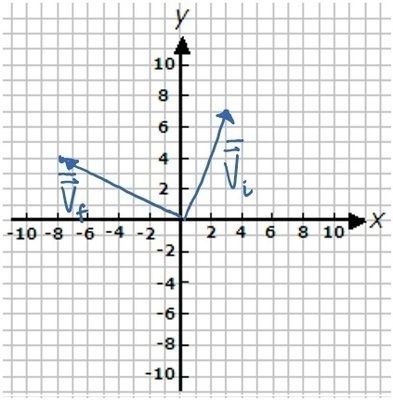
What is the magnitude of the average acceleration vector?
K-2D-12 Sketch the average acceleration vector on the blank plot if 0.5 seconds pass between the initial and final data points.
Note: Assume the grid spacing is 1 m for position vectors, 1 m/s for velocity vectors, and 1 m/s2 for acceleration vectors.
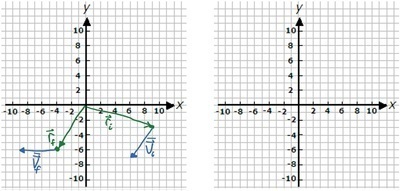
K-2D-13 The first stage of a trip has a displacement vector in the negative x direction. The second stage has a displacement at an angle of 30.0º above the positive x axis. The final stage has a displacement of magnitude 15 km and points in a direction 40.0º below the positive x axis. If after all three stages you end up where you started, what was the magnitudes of the displacement of the first two stages?
K-2D-14 A spaceship is traveling in the galactic northeast direction. The ship's thrusters then create a large constant acceleration in the southern direction. Which of the following statements are necessarily true regarding the time after the thrusters have fired.
1. The ship will be moving in the southeast direction.
2. The ship will eventually be moving in the southern direction
3. The ship's displacement will be in the southern direction
4. The ship will eventually be moving with both southern and eastern components
5. The change in the ship's velocity will be in the southern direction.
K-2D-15 A spaceship's controls fail for 5.00 s and during this time the thrusters on the ship give it an acceleration of 4.472 m/s2 in a direction 63.43 º from the positive x direction towards the positive y direction. They know that after the incident the ship was traveling with a speed of 15.81 m/s in a direction 18.43 º from the positive y direction towards the positive x direction. What are the final velocity and the average acceleration in Cartesian coordinates?
The information they've lost is their initial velocity and the change in position they underwent. Find those quantities.