M-COM-1 The two particles are both moving to the right. Particle 1 catches up with particle 2 and collides with it. The particles stick together and continue on with velocity vf. Which of these statements is true?
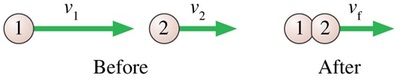
a. vf = v2
b. vf is less than v2
c. vf is greater than v2, but less than v1
d. vf = v1
e. vf is greater than v1
M-COM-2 An object is in free-fall near the surface of Earth. Which one of the following statements is true?
a. The object is in equilibrium.
b. The momentum of the object is conserved.
c. The object is isolated.
d. The impulse acting on the object is zero.
e. The change in momentum of the object is zero.
f. The change in the momentum during the 1st second is the same as during the 2nd second.
M-COM-3 Block A slides to the right with a speed v when it collides with block B traveling with the same speed in the opposite direction. After the collision block A's velocity has decreased by a factor of 3. If Block A is three times as massive as block B, how many times faster is block B moving than block A? Solve with either the vector representation or the mathematical representation.
M-COM-4 A mine car (mass = 440 kg) rolls at a speed of 0.50 m/s on a horizontal track, as the drawing shows. A 150-kg chunk of coal has a speed of 0.80 m/s sliding downward at an angle 25o from the horizontal when it leaves the chute and lands in the coal car.
Sketch the net momentum of the coal + car system, before the coal lands in the cart, using the head-to-tail method of addition. There should be three vectors on your diagram.
The net momentum of the coal + cart system appears to be down and the to the right before the coal lands in the cart and towards the right after. Which of the following statements about the coal + cart system can account for this phenomena.
a. The momentum is conserved
b. The system is isolated
c. The momentum is not conserved
d. The system is not isolated
e. The system is not large enough to justify conservation of momentum
Determine the velocity of the car/coal system after the coal has come to rest in the car.
M-COM-5 A spaceship of mass 2.0x106 kg is cruising at a speed of 5.0x106 m/s when the antimatter reactor fails, blowing up the ship in three pieces. One section, having a mass of 5.0x105 kg, is blown straight backward in the negative x-direction with a speed of 2.0x106 m/s. A second piece, with mass 8.0x105 kg, continues forward at an angle of 30° upward with respect to the original trajectory at 1.0x106 m/s. If the original spaceship was traveling in the +x direction, sketch a vector representing the direction of the third piece.
M-COM-11 A spaceship of mass 2.0x106 kg is cruising at a speed of 5.0x106 m/s when the antimatter reactor fails, blowing up the ship in three pieces. One section, having a mass of 5.0x105 kg, is blown straight backward in the negative x-direction with a speed of 2.0x106 m/s. A second piece, with mass 8.0x105 kg, continues forward at an angle of 30° upward with respect to the original trajectory at 1.0x106 m/s. What is the magnitude and direction of the velocity of the third piece after the explosion? (Answer: 1.471x107 m/s, 2.22° below original trajectory)
M-COM-6 A sports car weighing 500 kg and traveling at 27 m/s fails to stop at an intersection and crashes into a 1600 kg delivery truck traveling at 20 m/s in a direction at right angles to it. The wreckage becomes locked and travels 18 m before coming to rest. Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the road and the car + truck system during the sliding-to-rest stage. (Answer: 0.77)
How many stages should this problem be broken into?
The first stage of this problem should be dealt with using conservation of momentum. Which one of the following reasons most justifies that approach.
a. The energy of the collision is conserved.
b. No external forces act on the two during the collision.
c. No net external force act on the two during the collision.
d. The collision is assumed to be done so quickly that the impulse from friction can be neglected during the collision.
e. The two become locked together.
During the sliding to rest stage, identify all the types of physics that could be used to analyze the physics.
a. Kinematics
b. Mechanics (specifically forces)
c. Impulse
d. Conservation of Momentum
e. Work and Energy