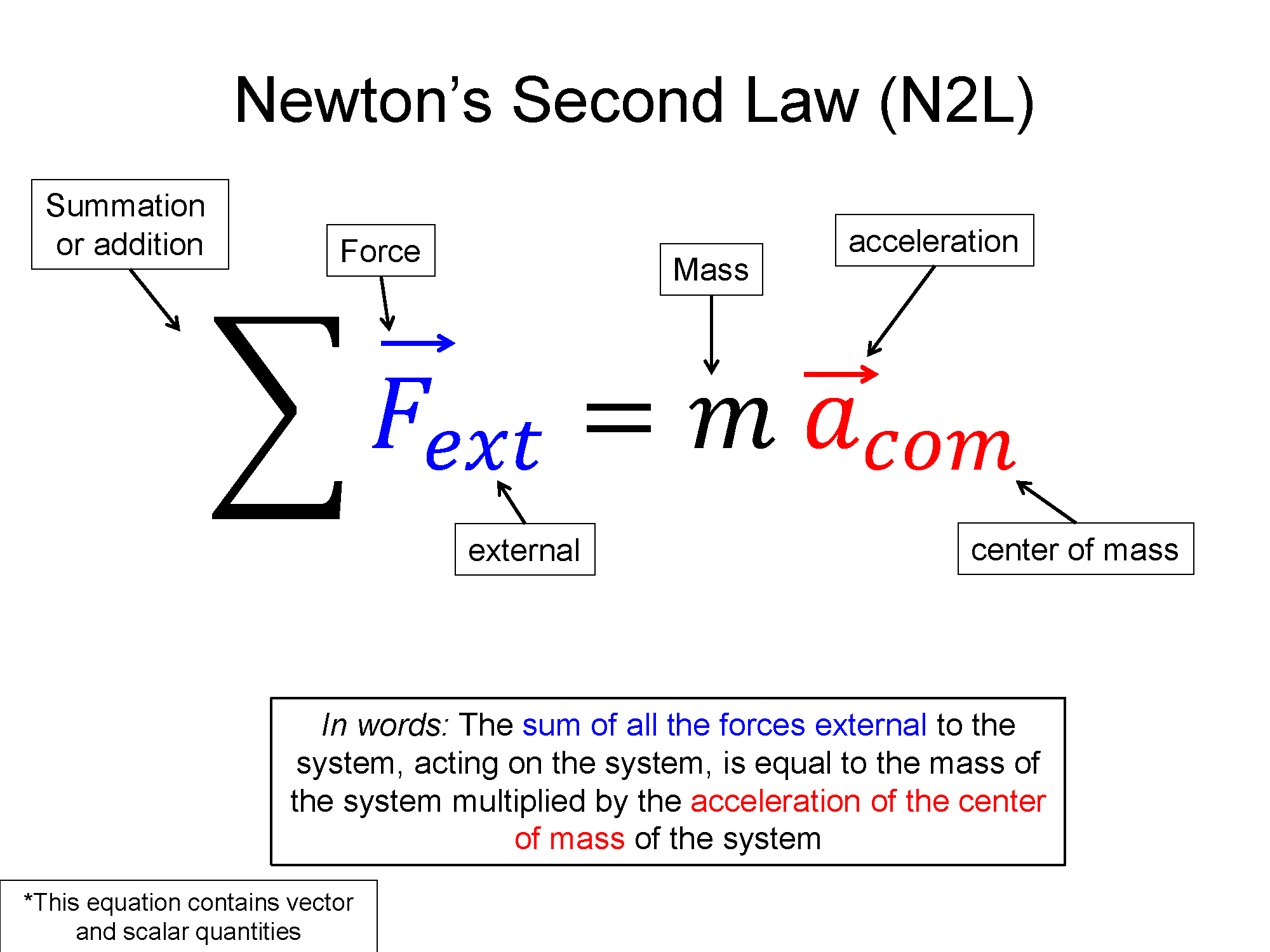
Newton's Second Law describes a force as proportional to acceleration, where the mass is the constant of proportionality. Free body diagrams are a method of visualizing and solving force problems.
Check out this NASA video introducing the concept of Newton's Second Law
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WzvhuQ5RWJE
NASA also discusses the concept of Newton's Third Law
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cP0Bb3WXJ_k
Pre-lecture Study Resources
Read the BoxSand Introduction and watch the pre-lecture videos before doing the pre-lecture homework or attending class. If you have time, or would like more preparation, please read the OpenStax textbook and/or try the fundamental examples provided below.
BoxSand Introduction
Newton's Laws | FBD and Newton's Second Law
Prior to this section, we did not ask any questions about what causes the motion of objects to begin or to change. In this section, we will use Newton's second law to develop a cause and effect relationship between forces and motion. Newton's second law can be stated as follows:
**NOTE: Just like kinematics, the rest of PH201 works under the point particle approximation. Thus, we will not need to worry about the center of mass yet. But in PH202, will will start to consider the physical shape of objects, requiring us to determine centers of mass.
Key Equations and Infographics
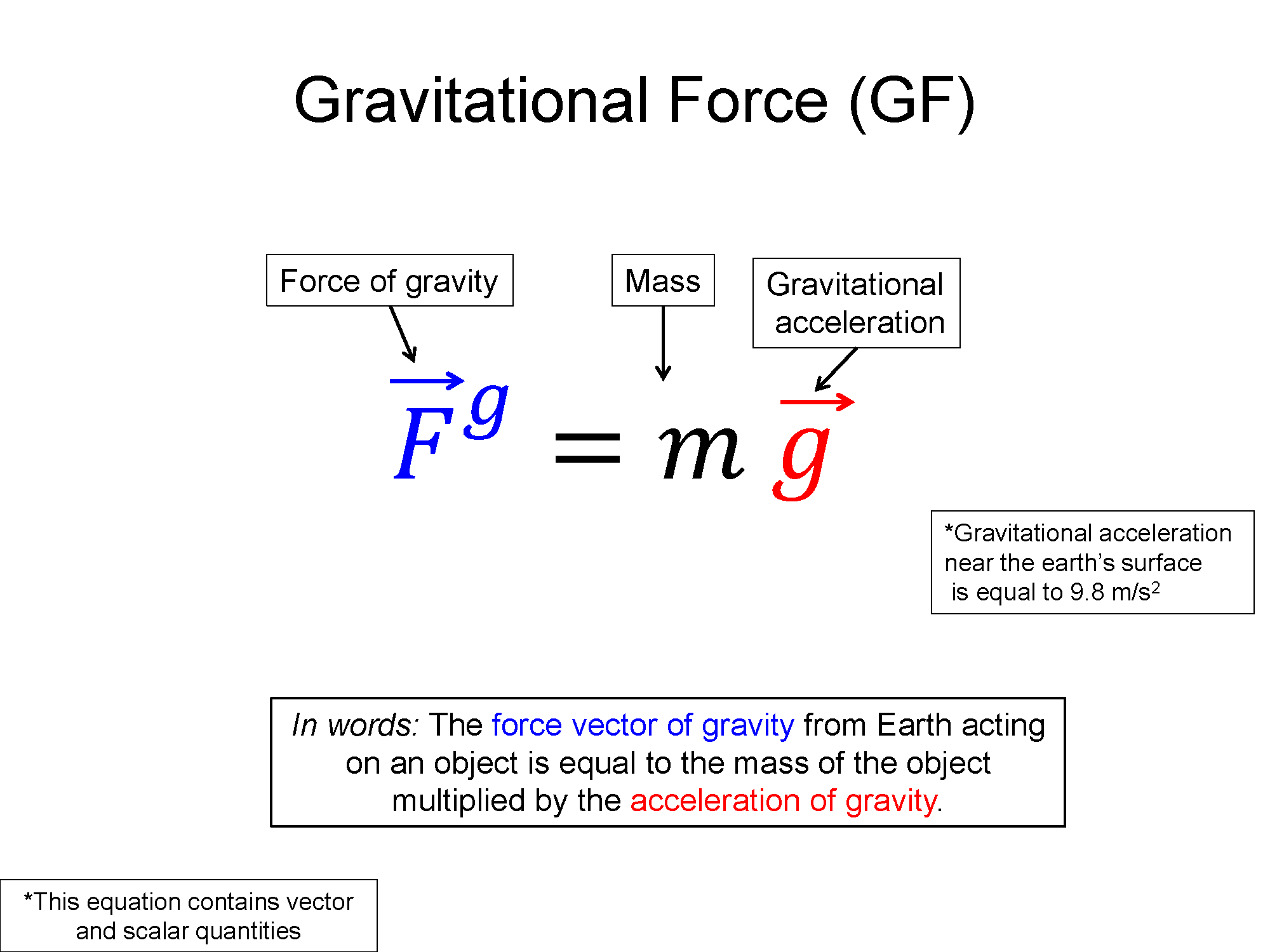
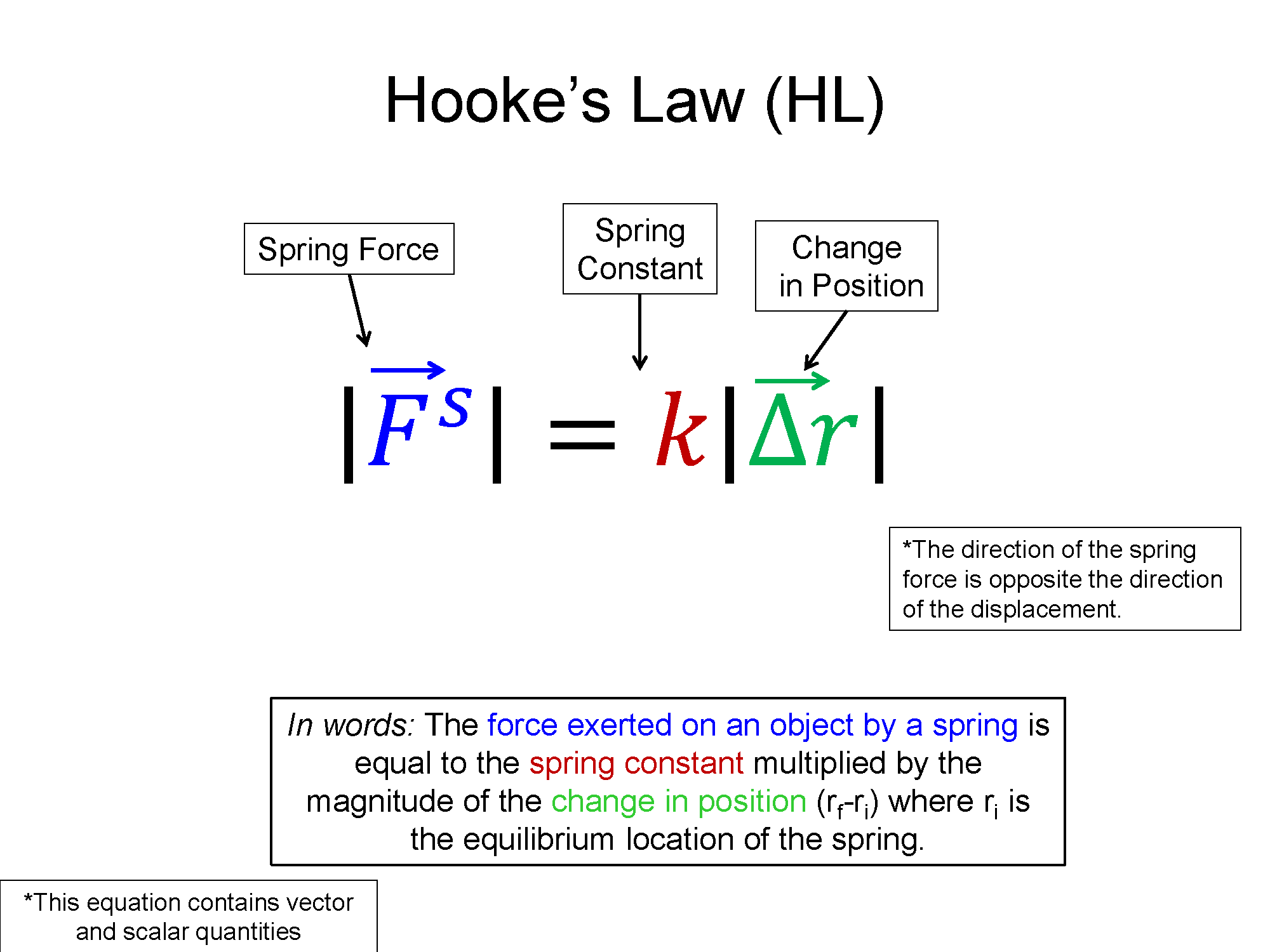
Now, take a look at the pre-lecture reading and videos below.
BoxSand Videos
Required Videos
Suggested Supplemental Videos
OpenStax Reading
OpenStax has some great problem solving strategies
__________________________ Previous Relevant Material __________________________
If you haven't read the previous sections on forces, the below links are from the previous lecture materials and may be necessary to understand the section above on problem solving strategies.
Here is an introduction to forces from the OpenStax textbook
OpenStax develops the force concept
Read about Newton's First Law of Motion
The most important law in forces is Newton's 2nd Law of Motion
The last of Newton's laws is the 3rd Law which talks about symmetry in forces.
Check out the normal force and tension
Fundamental examples
Recommended example practice problems
Set 1: Lifting a Piano, Playing in an Elevator
Set 2: Physics Classroom Laws of Motions
Set 3: Free Body Diagrams, and Other 2nd Law Problems
Post-Lecture Study Resources
Use the supplemental resources below to support your post-lecture study.
Practice Problems
BoxSand's Force Analysis Worksheet
BoxSand's Quantitative Practice Problems
BoxSand's Multiple Select Problems
For additional practice problems and worked examples, visit the link below. If you've found example problems that you've used please help us out and submit them to the student contributed content section.
Additional Boxsand Study Resources
Additional BoxSand Study Resources
Learning Objectives
Summary
The objective is introduce Newton's laws and apply the fundamentals of a force analysis. Specifically we focus on drawing free-body diagrams to facilitate translating the 2nd law to the mathematical representation. Connections to kinematics are also made.
Atomistic Goals
Students will be able to...
- Demonstrate the fact that a force is inherently an interaction between two objects or two systems.
- Explain Newton's 1st law as it relates to inertia.
- Explain Newton's 1st law and how it relates to the 2nd law.
- Define static and dynamic equilibrium.
- Explain Newton's 2nd Law.
- Explain Newton's 3rd Law force pairs.
- Define the point particle model
- Define a system(s) boundary and adhere their analysis to that boundary(s).
- Identify the type of forces interacting with your system and the direction they are applied.
- Differentiate between contact and non-contact forces.
- Demonstrate that the normal force is always perpendicular to the surface
- Draw a free-body-diagram (FBD) for the system(s).
- Demonstrate the ability to draw a properly scaled FBD.
- Draw the coordinate system that reduces the complexity of the vector analysis next to the FBD.
- Apply geometry to determine appropriate angles for the given coordinate system.
- Find the components of a force in the chosen coordinate system.
- Differentiate between A force and a NET force.
- Apply Newton's 2nd law in the mathematical representation.
- Differentiate between static and dynamic equilibrium.
- Differentiate between weight and apparent weight.
- Synthesize a force and kinematics analysis via the acceleration.
- Demonstrate that the net force points in the same direction as the acceleration
- Demonstrate the fact that the net force can be in the opposite direction of the motion.
YouTube Videos
Khan Academy's introduction to Newton's Second Law in a 2 part video sequence:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ou9YMWlJgkE
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=24vtg9Ehr0Q
Doc Schuster's introduction to Newton's Second Law part 1:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_Z7qivqbSBI
Doc Schuster's introduction to Newton's Second Law part 2:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_Z7qivqbSBI
Here is a really great video by Dr. Davies from Gordon State College that relates a physics problem, Newton's Second Law, and FBD:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NDiQ363uBj8
Other Resources
This link will take you to the repository of other content related resources.
Simulations
This PHet simulation allow you to view changing magnitudes of the force vectors in a FBD;
This is a nice tool that will help you understand how to construct free body diagrams
Here is a simple interactive to help you understand how to properly arrange force vectors,
For additional simulations on this subject, visit the simulations repository.
Demos
Low Friction Atowood Machine demo,
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4ovhEkSIqV0
Pasco dunamics cart and track: Forces, Mass, and Acceleration connection to Newton's 2nd law,
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aDLYpJoSRhM
For additional demos involving this subject, visit the demo repository
History
Oh no, we haven't been able to write up a history overview for this topic. If you'd like to contribute, contact the director of BoxSand, KC Walsh (walshke@oregonstate.edu).
Physics Fun
Oh no, we haven't been able to post any fun stuff for this topic yet. If you have any fun physics videos or webpages for this topic, send them to the director of BoxSand, KC Walsh (walshke@oregonstate.edu).
Other Resources
Here is a concise explanation of Newton's Second Law:
Resource Repository
This link will take you to the repository of other content on this topic.
Problem Solving Guide
Use the Tips and Tricks below to support your post-lecture study.
Assumptions
As we get more forces on our free-body diagrams, it becomes more and more important to think about the physical situation. Will the object move in the y-direction? No? Then all the forces in the y MUST cancel out. If they don’t it means we accelerate in that direction per F=ma.
Normal force will always point directly away from the object generating it, at a 90-degree angle from the surface of the object creating the external force.
Checklist
Misconceptions & Mistakes
- Don't be tricked into thinking that if the net force is 0, the object isn't moving, it could still be moving but not accelerating (i.e. moving with a constant velocity).
- Often accelerating objects will move in directions that they aren't accelerating in. This is because if they have an initial velocity, they will move in the inital velocity's direction immediately, but over time will forced into moving in the direction of the acceleration. Given enough time under the same constant force, an object will eventually move in the direction of its acceleration.
- The Difference Between Mass and Weight Veritasium video:
Pro Tips
- Generally, it most advisable to think about tilting your coordinate system so one access points in the direction of acceleration if there is one. This results in one direction’s sum of forces being equal to mass times that direction’s acceleration, while the other direction’s sum of forces will equal 0. If there is no acceleration, it is often best to tilt to make your axes align so you have to decompose the fewest vectors, in other words, tilt so that most or all of your arrows are sitting on the two axes.
- Everytime you sum forces, it will usually result in one of 3 situations: 1) it equal 0, meaning a=0 and the object is not moving in that direction. 2) It will equal mass times acceleration where acceleration is non-zero and the object IS moveing. Or 3) it will equal another force (this is more for later). This critically about what is happening in the physical situation after you sum your forces and make the correct choice of what to set them equal to (and a sum of forces is only useful if you set it equal to SOMETHING, and to do that, you ned to make a physical assumption).
Multiple Representations
Multiple Representations is the concept that a physical phenomena can be expressed in different ways.
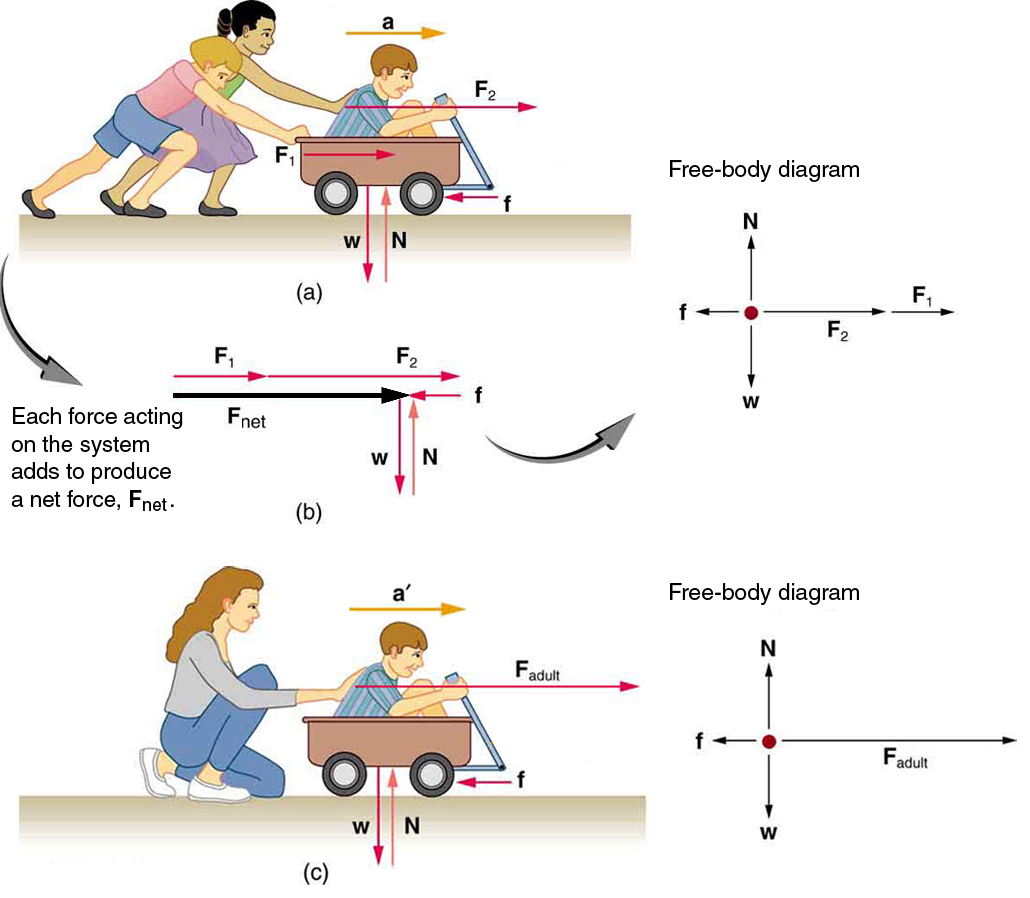
Physical
Mathematical
The main mathematical representation for forces will be applying Newton's Second Law to a physical problem. You will need to analyze the motion of an object and create a free body diagram of the relative forces in order to derive the force equations. We learned in the kinematics section how to analyze motion without any concern about the forces that caused the motion. The infographic below describes the relationship between force and acceleration. Thus, we may now analyze the forces acting on an object to determine the relative acceleration.
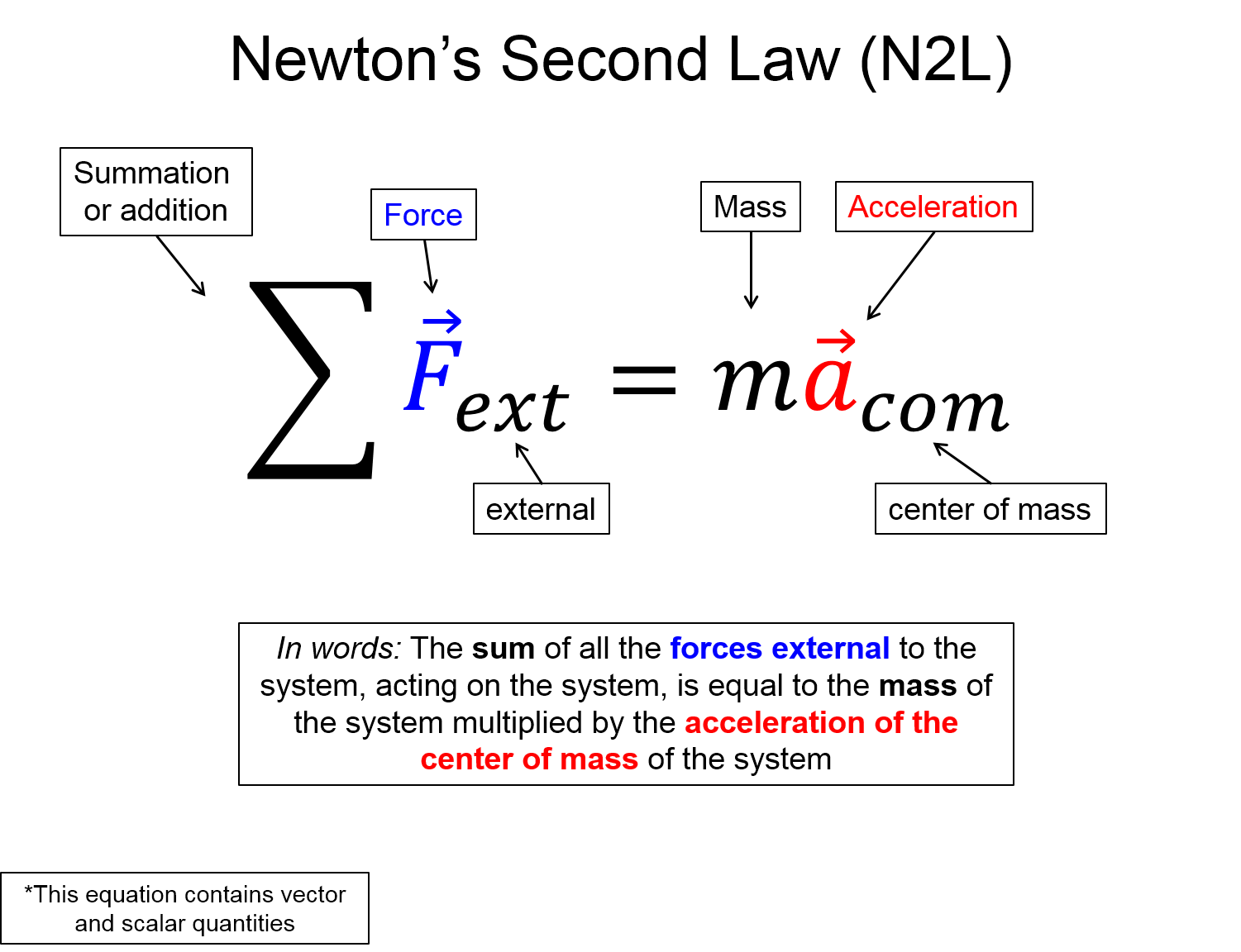
Graphical
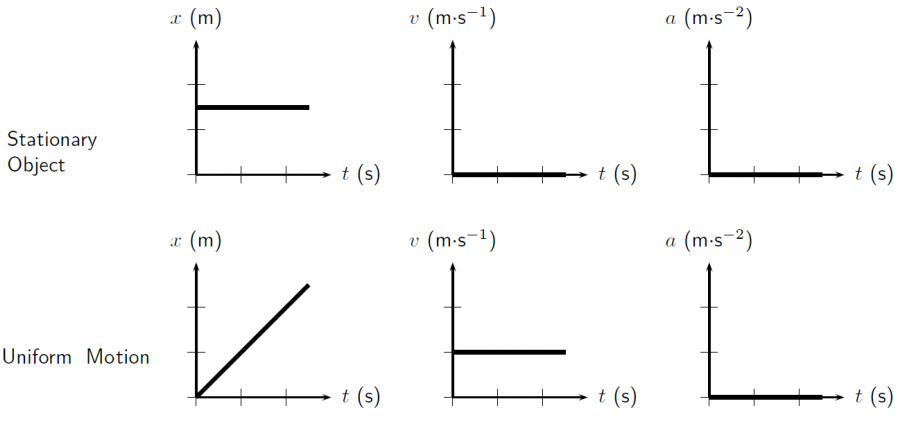
Descriptive
A spaceship, deep in space, has ran out of fuel. Since nothing is there to act on the ship, it will continue to move at the speed it is moving and in the direction it is moving. It will do this until something acts on it, something like the pull from a nearby star that becomes no longer negligible as the ship passes near the star.
Experimental
Here is a great video of an experiment where a pen cap is dropped into a bottle using Newton's first law