BoxSand's Resources
Introduction
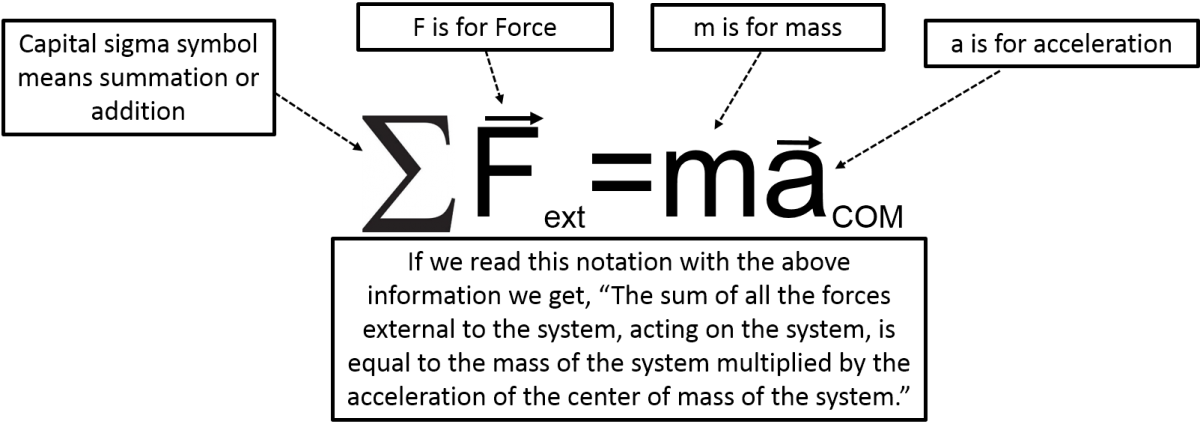
Newton's second law says that the sum of all of the external forces on a system must be equal to the mass of the system times the acceleration of the center of mass of the system. Newton's second law is often used to identify unknown forces or connect net forces to acceleration. With the acceleration, kinematics can be used to understand motion. We will need a number of tools to use Newton’s second law such as Free Body Diagrams and Newton’s Third Law.
Videos
Pre-lecture videos
Newton's Laws (6 min)
https://media.oregonstate.edu/media/t/0_ta9bhwiy
Equilibrium Example - Kitty Picture (7 min)
https://media.oregonstate.edu/media/t/0_l0dxbt04
Equilibrium Example - Skydiver (6 min)
https://media.oregonstate.edu/media/t/0_8hlqo30w
Supplemental but suggested
Equilibrium Example - Wolves 2D Tug-O-War (10 min)
https://media.oregonstate.edu/media/t/0_zyb5t982
Non-Equilibrium Example - skiing (7 min)
https://media.oregonstate.edu/media/t/0_6hgudjgd
Tension Up a Chain Example (13 min)
https://media.oregonstate.edu/media/t/0_hnf2gkpm
Web Resources
Text
Here is a concise explanation of Newton's Second Law:
This is a comprehensive introduction to Newton's Second Law that covers how to deal with Newton's Second Law and systems. This online textbook discusses Newton's Second Law with diagrams, worked problem examples, and interactive conceptual questions. All notation in this text is consistent with BoxSand's:
Other Resources
This link will take you to the repository of other content related resources.
Videos
Khan Academy's introduction to Newton's Second Law in a 2 part video sequence:
Doc Schuster's introduction to Newton's Second Law part 1:
Doc Schuster's introduction to Newton's Second Law part 2:
Here is a really great video by Dr. Davies from Gordon State College that relates a physics problem, Newton's Second Law, and FBD:
Other Resources
This link will take you to the repository of other content related resources.
Simulations
Here is a PhET simulation relating force and motion:
Another simple tool to look at forces and acceleration by PhET. This simulation uses FBD on the right, make sure you are familiar with that tool. It might be best to turn friction off initially:
(requires download)
For additional simulations on this subject, visit the simulations repository.
Demos
Low Friction Atowood Machine demo,
Pasco dunamics cart and track: Forces, Mass, and Acceleration connection to Newton's 2nd law,
For additional demos involving this subject, visit the demo repository
Practice
Fundamental examples
1. A $2 \, kg$ experiences a net force of $\sum \vec{F} = \langle 1,3,4 \rangle \, N$. What is the acceleration of this object?
2. A $5 \, kg$ object sits on top of a frictionless table with a force pushing it to the right as shown in the image below. If the magnitude of the force of push is $4 \, N$, what is the acceleration of the object?

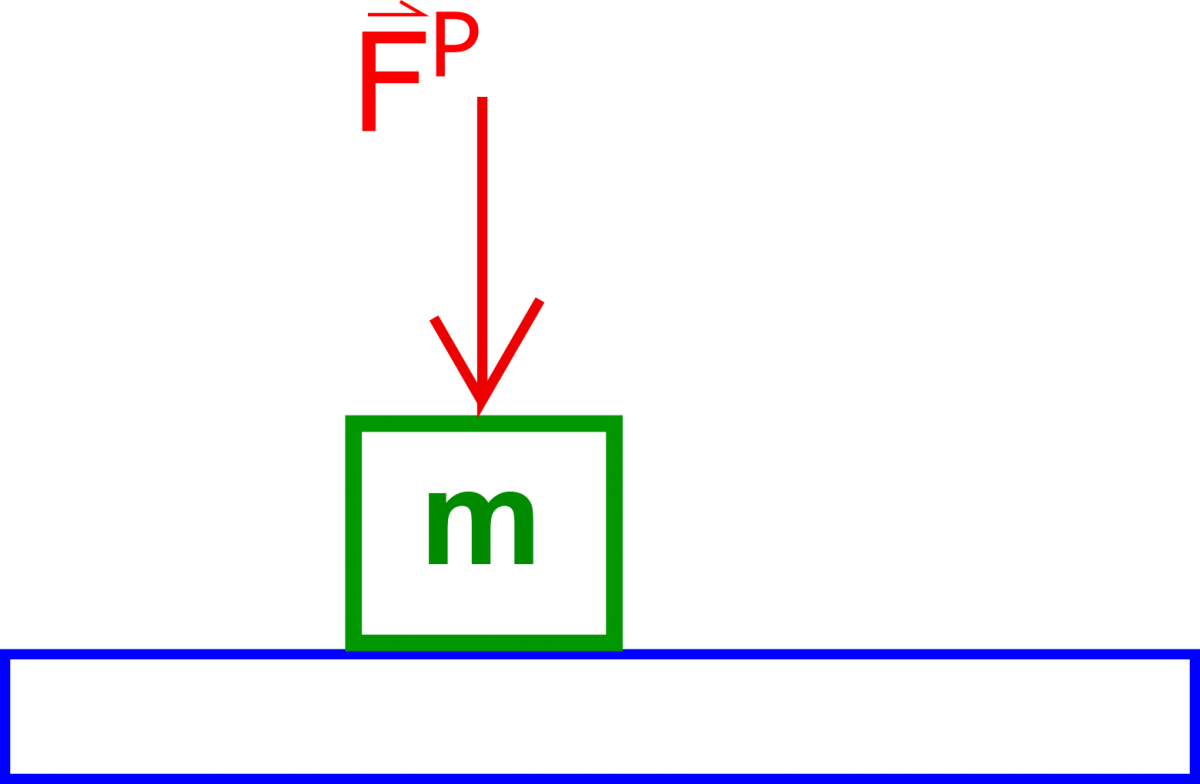
3. A $5 \, kg$ object is in static equilibrium while sitting on top of a table with a force pushing it straight downward as shown in the image below. If the magnitude of the force of push is $4 \, N$, what is the normal force between the table and the object?
CLICK HERE for solutions.
Short foundation building questions, often used as clicker questions, can be found in the clicker questions repository for this subject.
Practice Problems
BoxSand's Quantitative Practice Problems
BoxSand's Multiple Select Problems
Recommended example practice problems
Set 1: Lifting a Piano, Playing in an Elevator
Set 2: Physics Classroom Laws of Motions
Set 3: Free Body Diagrams, and Other 2nd Law Problems
For additional practice problems and worked examples, visit the link below. If you've found example problems that you've used please help us out and submit them to the student contributed content section.