Atoms are comprised of charges. The positively charged nucleus is attracted to the negatively charged electrons. Molecules, which are comprised of atoms, also bind together due to this charge related force of attraction. Solids and liquids, comprised of molecules, also bind together due to the electric force of charges. All forces we experience, except gravity, are due to the electric force.
Crash Crouse physics introduces us to charges.
Pre-lecture Study Resources
Watch the pre-lecture videos and read through the OpenStax text before doing the pre-lecture homework or attending class.
BoxSand Introduction
Electric Phenomena | Coulomb's Law
Electric Force
To understand the effects of objects with a distribution of charges exerting a force on each other, lets start with the force between two point charges. This is known as Coulomb's Law. The below equation reads, the magnitude of the electric force of particle 2 on 1 is equal to the magnitude of the electric force of 1 on 2 (Newton's 3rd law). That force is equal to the electric constant $k$ times the magnitude of $q_1$, times the magnitude of $q_2$, divided by the absolute distance between $q_1$ and $q_2$ squared.
$|\overrightarrow{F}^E_{21}| = |\overrightarrow{F}^E_{12}| = \frac{k|q_1||q_2|}{|\Delta \overrightarrow{r}_{12}^2|}$, where $k=8.99\times 10^9 N \cdot m^2/C^2$
The direction of the net force is determined by drawing a Free-Body Diagram and using the fact that unlike charges attract and like charges repel.
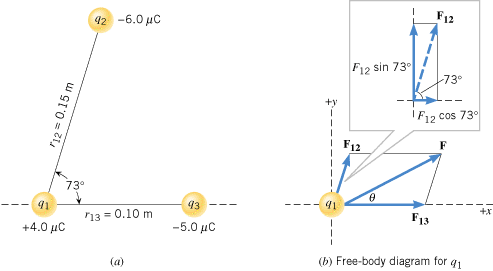
Here you see an example of the FBD for $q_1$ interacting with $q_2$ and $q_3$. Since 1 is positively charged and 2 and 3 are both negatively charged, 1 is attracted to both 2 and 3. So both $F_{12}$ and $F_{13}$, acting on particle 1, are towards the other particle. The magnitude of $F_{13}$ is larger than $F_{12}$ even though $q_2$ has a greater charge. That is due to $q_3$ being closer to $q_1$ than $q_2$. With the electric force being inversely proportional to the distance between the particles and only proportional to the charge to the 1st power, being closer means a greater force in this case.
To find the force on a charged particle you typically have to do the following:
- Draw a FBD of forces acting on the particle of interest using whether they attract or repel and a rough scaling of how large due to the relative charge magnitudes and distances.
- Determine the distance between the particle of interest and each other particle.
- Determine the magnitude of each electric force.
- Use vector summation to add up the components of each electric force and find the net force. You may have to use an angle found using geometry of the physical setup to find a component of the force.
Key Equations and Infographics
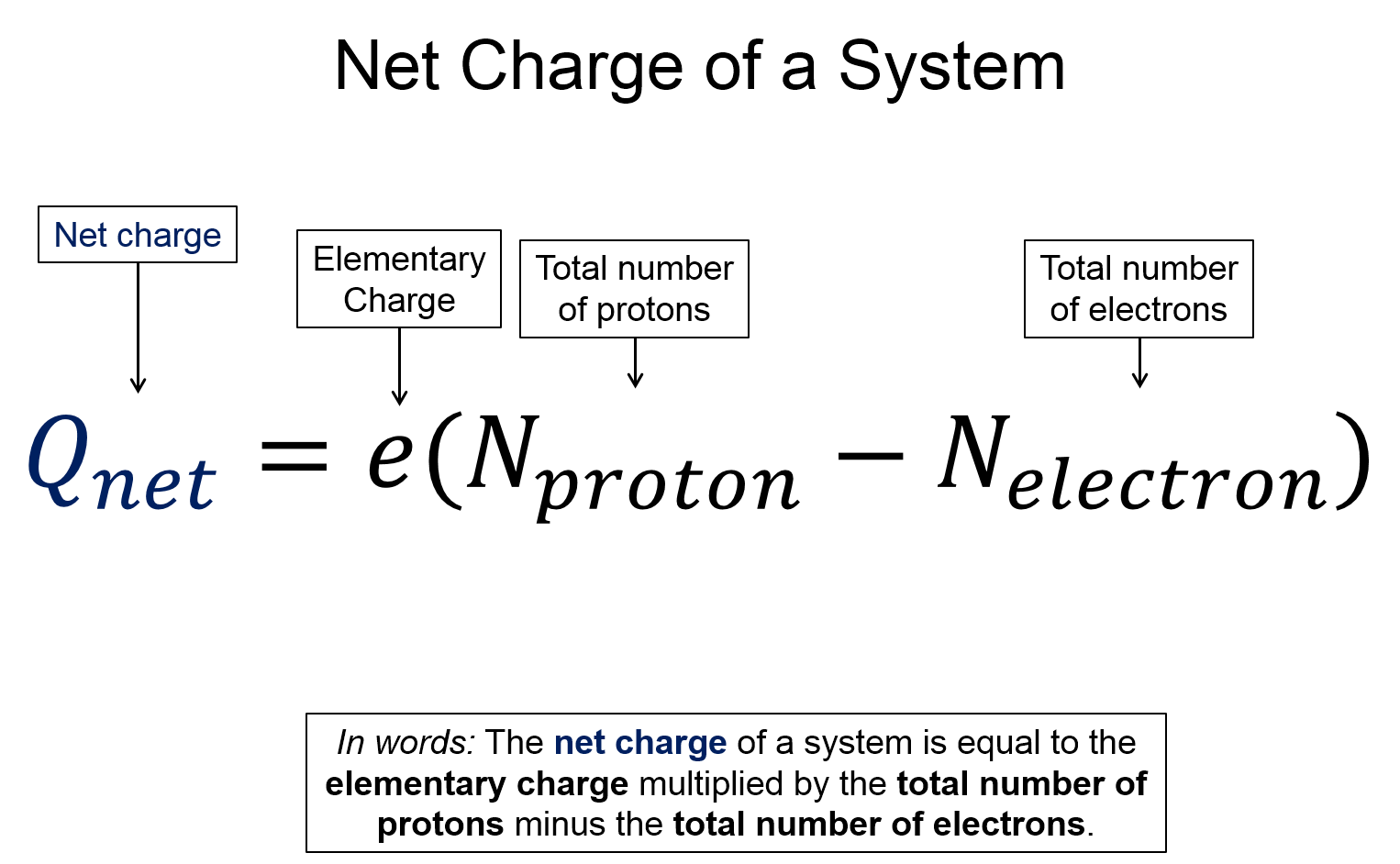
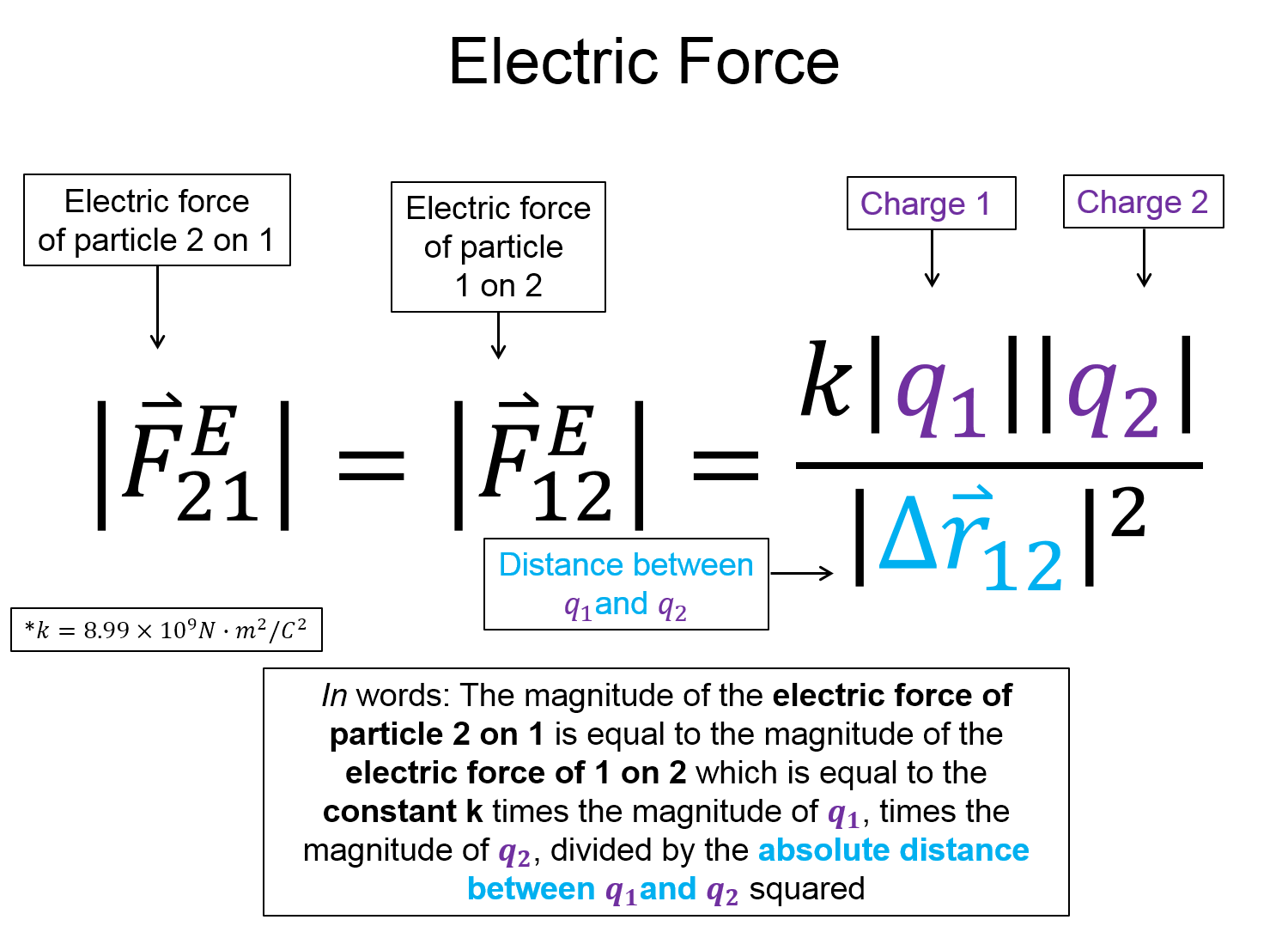
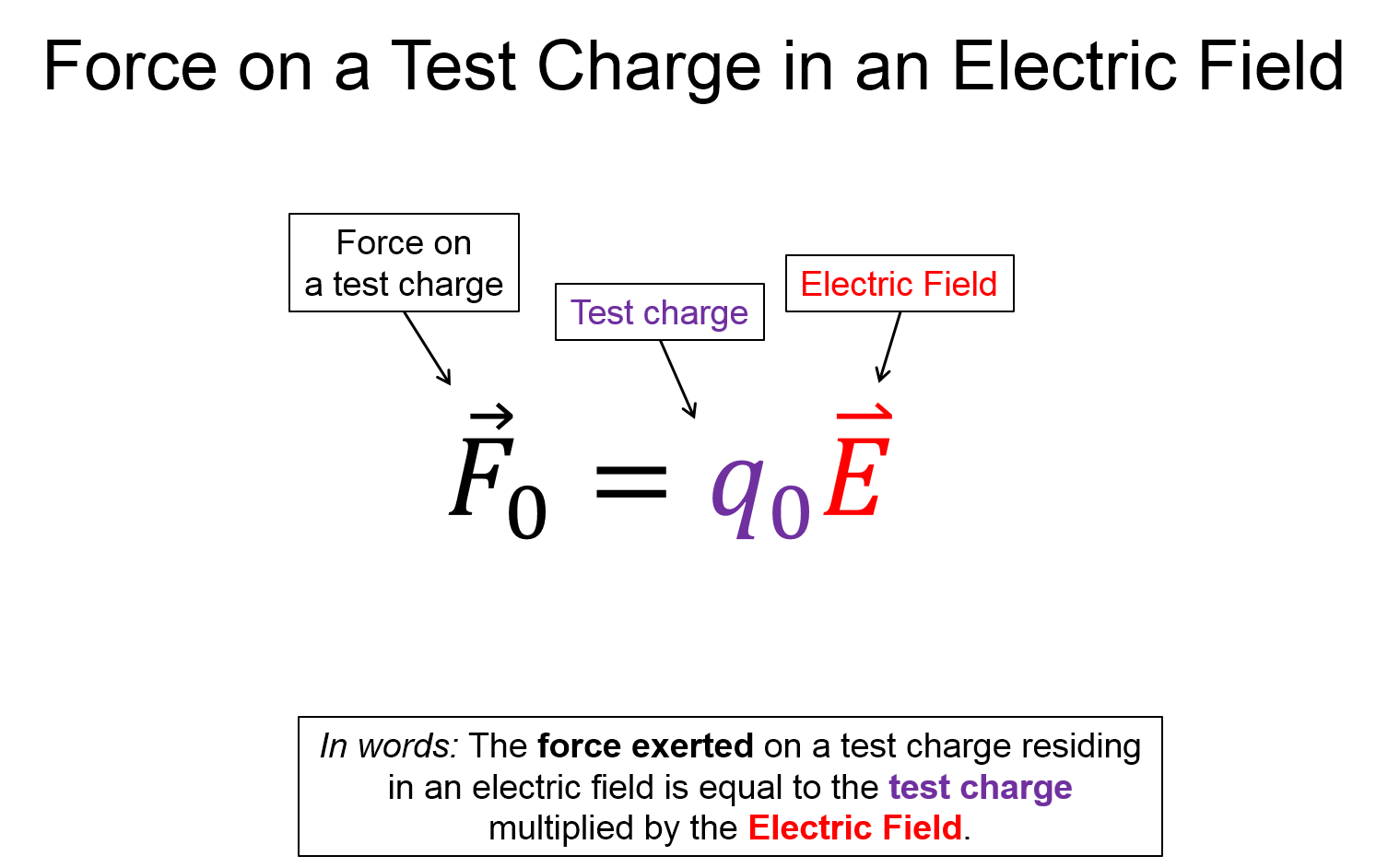
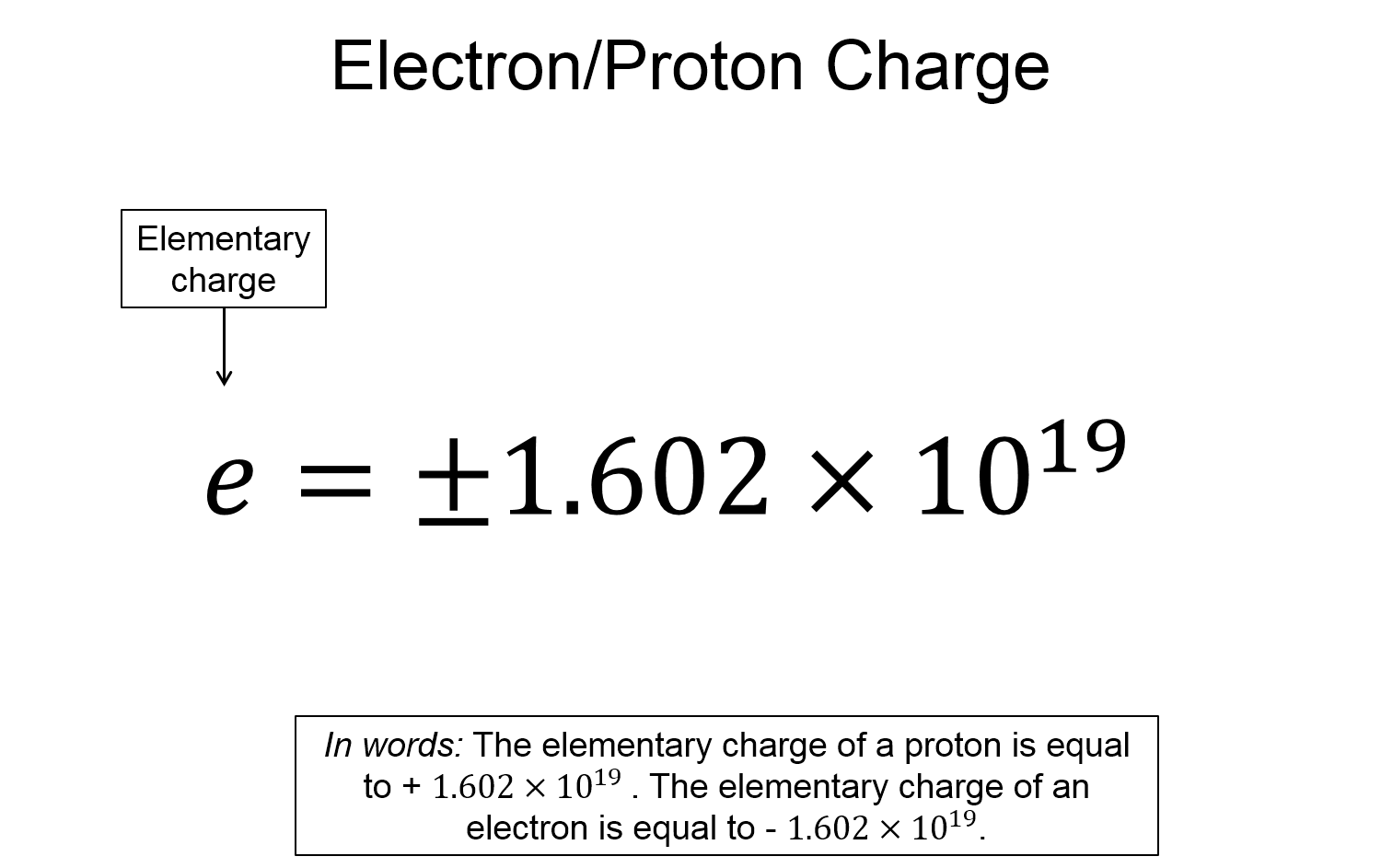
Now, take a look at the pre-lecture reading and videos below.
BoxSand Videos
OpenStax Reading
Fundamental examples
(1) A point charge with charge $q_1 = 1.8 nC$ is located at the origin. A point charge with charge $q_2 = 3.6 nC$ is located a distance $r_{12} = 6 nm$ away. (a) What is the magnitude of the coulomb force from charge 1 on charge 2? (b) Is this an attractive or repulsive force?
(2) A point charge with charge $q_1 = - 1.8 nC$ is located at the origin. A point charge with charge $q_2 = 3.6 nC$ is located a distance $r_{12} = 6 nm$ away. What is the magnitude of the coulomb force from charge 1 on charge 2?
(3) A point charge with charge $q_1 = - 1.8 nC$ is located at the origin. A point charge with charge $q_2 = 3.6 nC$ is located a distance $r_{12} = 6 nm$ away. A point charge with charge $q_3 = 5 nC$ is located at a position $r_3 = <2,2> nm$. What is the magnitude of the coulomb force from charge 1 on charge 2?
Solutions found HERE
Short foundation building questions, often used as clicker questions, can be found in the clicker questions repository for this subject.
Post-Lecture Study Resources
Use the supplemental resources below to support your post-lecture study.
Practice Problems
BoxSand practice problems - Answers
BoxSand's multiple select problems
BoxSand's quantitative problems
Recommended example practice problems
- OpenStax, Period and Frequency also linked in Charges & the Electric Force sections.
- Static Electricity and Charge, Website Link
- Conductors and Insulators, Website Link
- Coulomb's Law, Website Link
- Large set of questions on electric charge and force. External PDF
- Coulomb's Law Review, External PDF
For additional practice problems and worked examples, visit the link below. If you've found example problems that you've used please help us out and submit them to the student contributed content section.
Additional Boxsand Study Resources
Additional BoxSand Study Resources
Learning Objectives
Summary
Summary
Atomistic Goals
Students will be able to...
YouTube Videos
Pre-Med Academy is back with three well put together videos on our main subjects, Electric Charge, Electric Force, and Coulomb's Law
Youtube: Pre-Med Academy - Coulomb's Law
Step By Step Science has several example problems, here are a few on using Coulomb's Law. There are more in this section's content repository.
Other Resources
This link will take you to the repository of other content related resources .
Simulations
This simulation by Duffy helps you with Coulombs Law and Newton's 2nd law
The colorado PhET simulation is everything you ever needed in life, that you didn't know that you needed. We present to you, John Travoltage.
Charge transfer PhET simulation with baloons and a sweater.
For additional simulations on this subject, visit the simulations repository.
Demos
Rub a plastic cup against carpet, hair, or fur, and observe the effects of the net charge now on the cup.

For additional demos involving this subject, visit the demo repository
History
Oh no, we haven't been able to write up a history overview for this topic. If you'd like to contribute, contact the director of BoxSand, KC Walsh (walshke@oregonstate.edu).
Physics Fun
Surface tension is a polarization force between atoms. It's responsible for holding a water droplet together.

Play with John Travolta's leg and arm to get a Travoltage.
Other Resources
Boston University's Page on electric charge and Coulomb's law is neat reference with a couple of example problems
PPLATO is a complete resource with a lot of information, and several practice questions per subject. This webpage covers electric charge, the electric field, and electric potential, frocus on the electric charge, we'll get back around to field and potential later.
The Physics Classroom has an entire chapter on static electricity. The last lesson of the chapter is on Electric Fields so save that for later!
Resource Repository
This link will take you to the repository of other content related resources .
Problem Solving Guide
Use the Tips and Tricks below to support your post-lecture study.
Assumptions
Checklist
Misconceptions & Mistakes
- If you have two charges QQ and qq, and the magnitude of charge QQ is greater than that of charge qq, the two charges still apply an equal and opposite force to each other. Regardless of the relative magnitudes, Newton's 3rd Law still holds.
- While you can induce a dipole in both insulators and conductors, the atomic nature of the dipole is different for the two cases.
Pro Tips
Multiple Representations
Multiple Representations is the concept that a physical phenomena can be expressed in different ways.
Physical
Mathematical
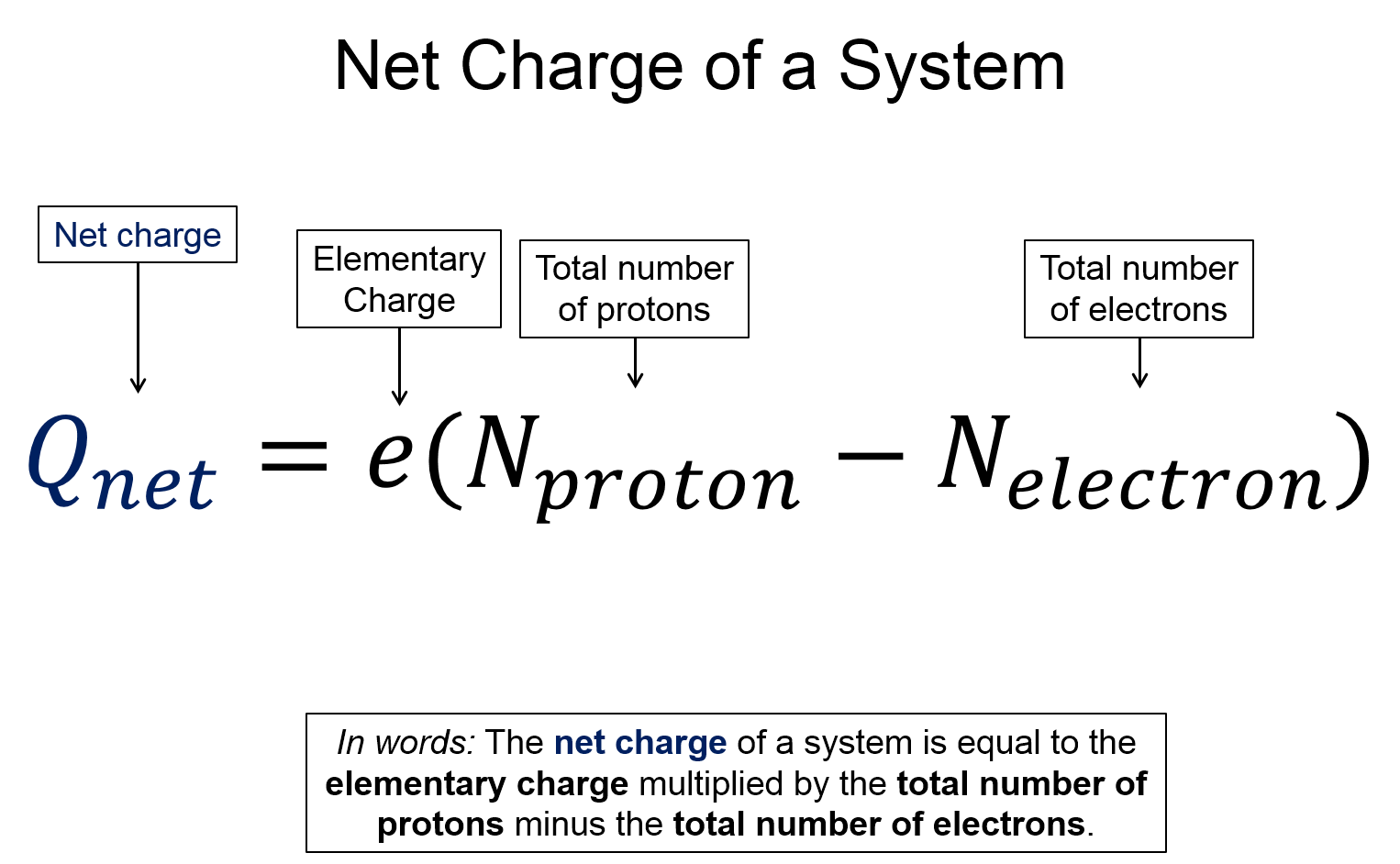



Graphical
Descriptive
Experimental
