A cathode ray tube creates a stream of electrons you can see. These electrons are deflected in their motion when they travel through a magnetic field. Check it out in the video below!
Pre-lecture Study Resources
Watch the pre-lecture videos and read through the OpenStax text before doing the pre-lecture homework or attending class.
BoxSand Introduction
Subject | Lecture
Key Equations and Infographics
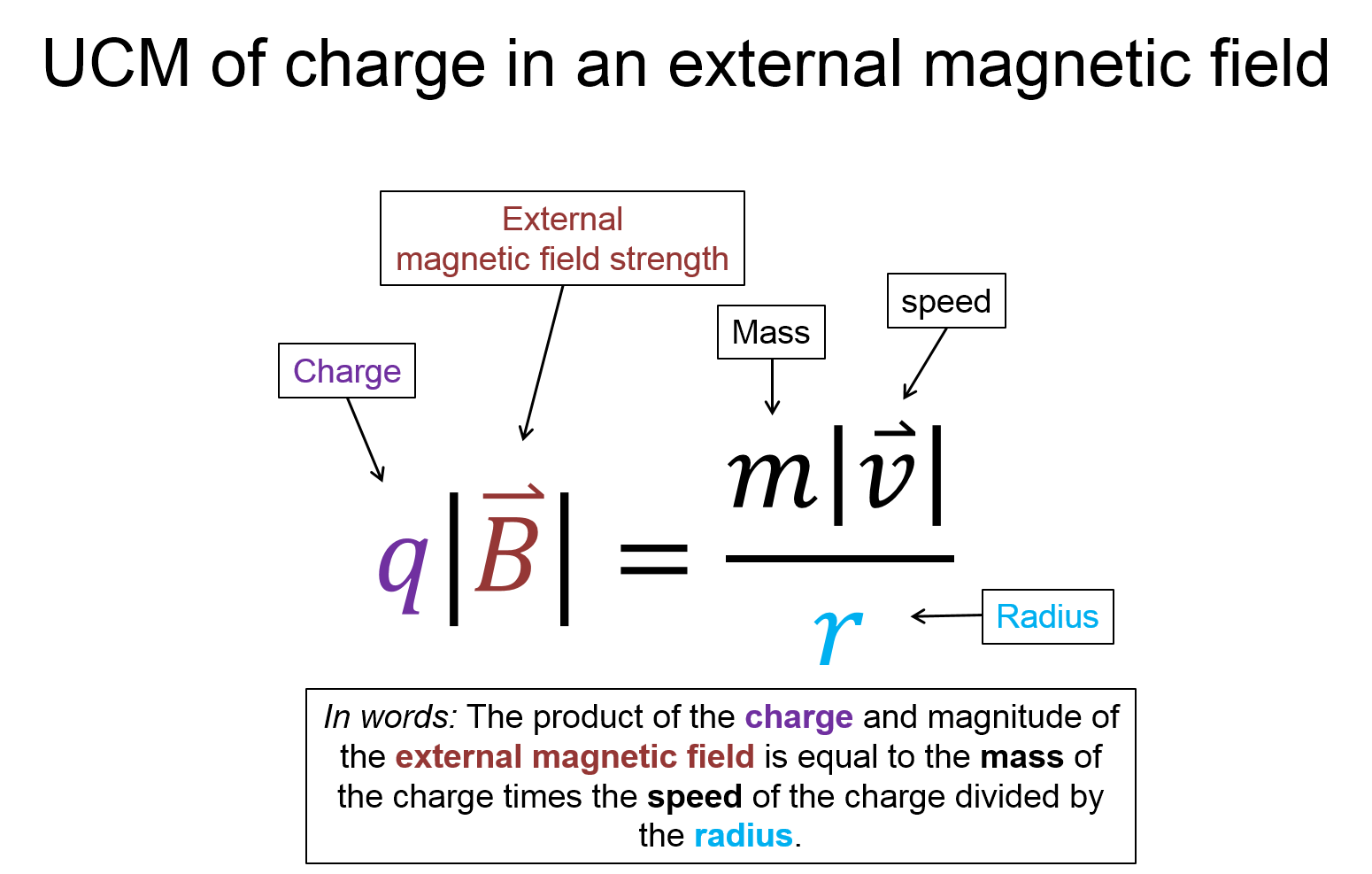
Now, take a look at the pre-lecture reading and videos below.
BoxSand Videos
Required Videos
Suggested Supplemental Videos
OpenStax Reading
OpenStax Section 22.4 | Magnetic Field Strength: Force on a Moving Charge in a Magnetic Field
OpenStax Section 22.5 | Force on a Moving Charge in a Magnetic Field: Examples and Applications
OpenStax Section 22.6 | The Hall Effect
OpenStax Section 22.7 | Magnetic Force on a Current-Carrying Conductor
OpenStax Section 22.8 | Torque on a Current Loop: Motors and Meters
OpenStax Section 22.10 | Magnetic Force between Two Parallel Conductors
OpenStax Section 22.11 | More Applications of Magnetism
Fundamental examples
Short foundation building questions, often used as clicker questions, can be found in the clicker questions repository for this subject.
(1) A proton traveling in the $+\hat{x}$ direction with a speed of $4.3 \cdot 10^{6} \frac{m}{s}$ enters a uniform magnetic field pointing in the $+\hat{z}$ direction with field strength $B = 2 T$. How many revolutions does the proton undergo in 2 seconds? Assume that once the proton enters the magnetic field, it never leaves it.
Post-Lecture Study Resources
Use the supplemental resources below to support your post-lecture study.
Practice Problems
BoxSand practice problems
Recommended example practice problems
- Openstax, go to the bottom of the page and work through the conceptual problems and provided practice exercises. Website Link
- LibreTexts has a large amount of practice and conceptual problems at the bottom of the section. Website Link
For additional practice problems and worked examples, visit the link below. If you've found example problems that you've used please help us out and submit them to the student contributed content section.
Additional Boxsand Study Resources
Additional BoxSand Study Resources
Learning Objectives
Summary
Summary
Atomistic Goals
Students will be able to...
YouTube Videos
PHYSIERGE shows an awesome experiment using an electron gun and two large magnets to show the circular path of a stream of electrons.
MathPhysicsQuestions has a short lecture on UCM then an example finding the radius and period of motion.
7activestudio gives a nice leacture on motion in an electric field with good visuals.
Other Resources
This link will take you to the repository of other content related resources for uniform circular motion in magnetic fields.
Simulations
Demos
History
Physics Fun
Other Resources
Resource Repository
Boundless's section is shorter than the Openstax section and uses a cyclotron example after introducing the material. The second section from Boundless shows different examples and applications, continuing with the cyclotron, and including mass spectroscomers and magnetrons.
| Primary Text | Examples and Applications |
Libretext's section gives an example of how to find the period of the election as well as exploring more difficult concepts such as helical motion.
Lecture slides used at De Anza College to cover the basics and a few examples.
Other Resources
This link will take you to the repository of other content related resources for uniform circular motion in magnetic fields.
Problem Solving Guide
Use the Tips and Tricks below to support your post-lecture study.
Assumptions
Checklist
Misconceptions & Mistakes
Pro Tips
Multiple Representations
Multiple Representations is the concept that a physical phenomena can be expressed in different ways.
Physical
Mathematical

Graphical
Descriptive
Experimental