Check out this trailer video from OpenStax about the Moment of Inertia.
Pre-lecture Study Resources
Watch the pre-lecture videos and read through the OpenStax text before doing the pre-lecture homework or attending class.
BoxSand Introduction
Statics and Dynamics | Dyamics and Moment of Inertia
Dynamics involves applying Newton's 2nd Law for rotation.
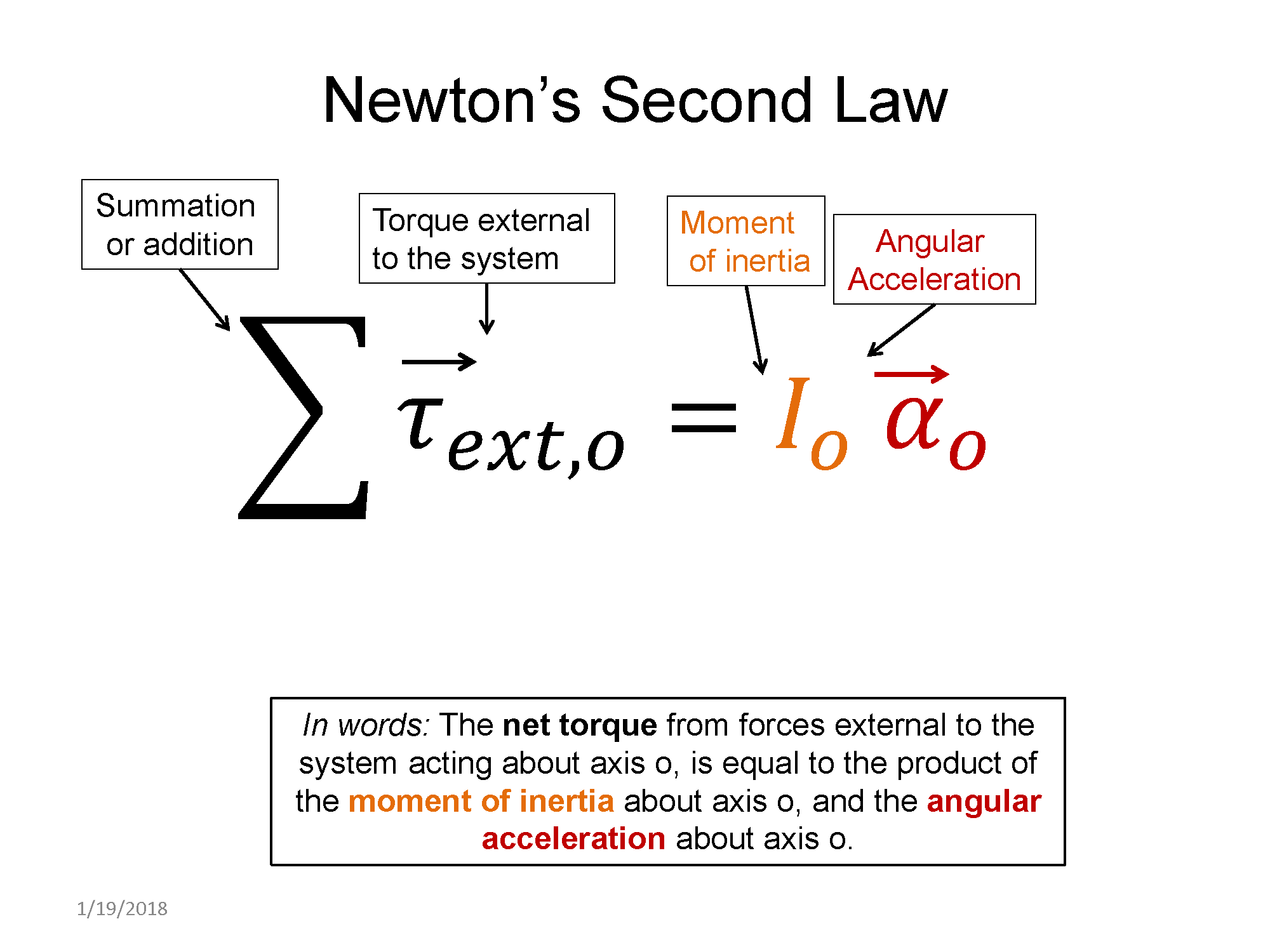
In a system that is not in rotational equilibrium, the angular acceleration is not zero. This results in the RHS (right-hand side) of the 2nd law to not be zero. You will need to know the moment of inertia for a mass distribution. Below are the equations for a the moment of inertia for some common mass distributions.
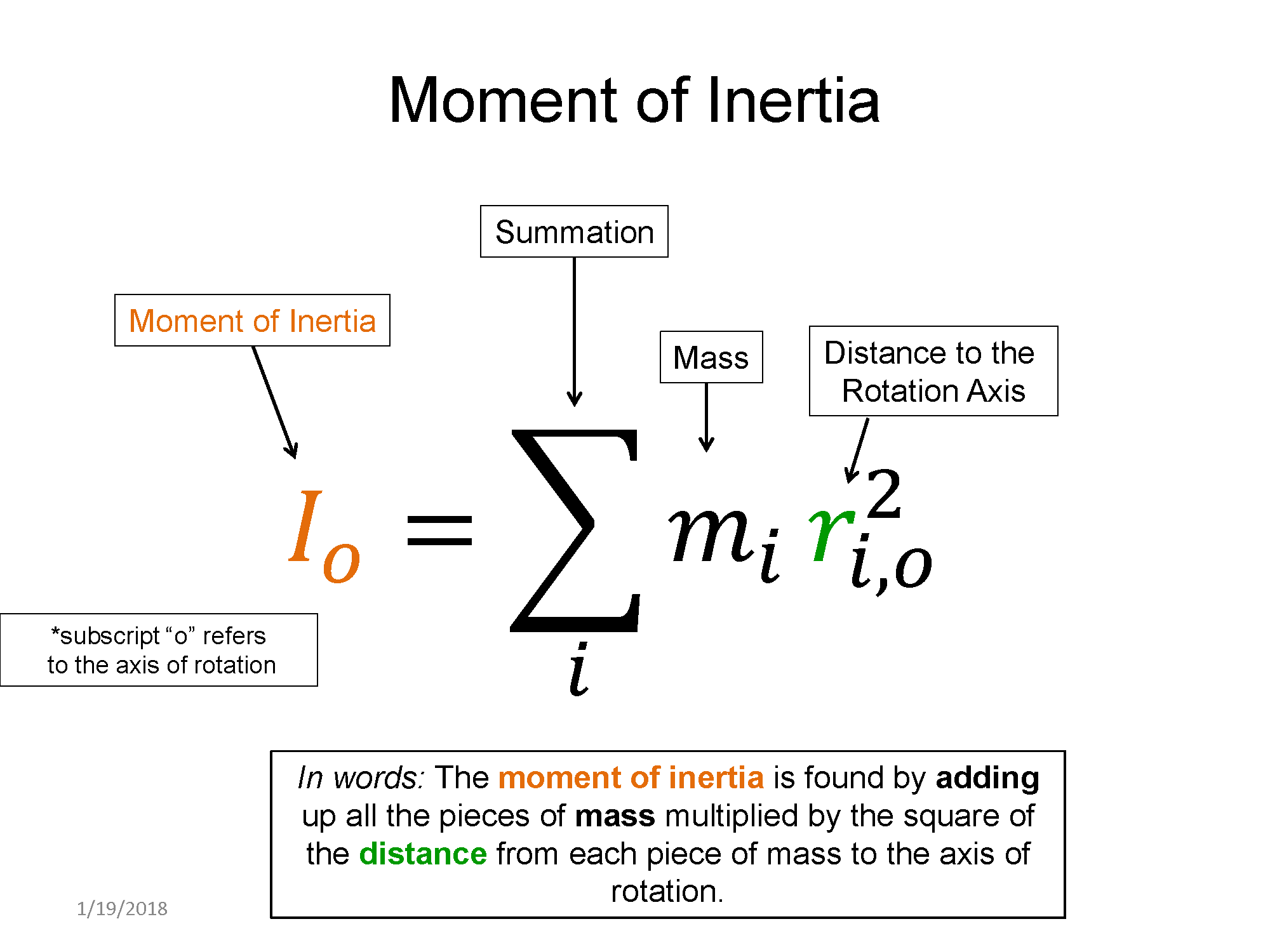
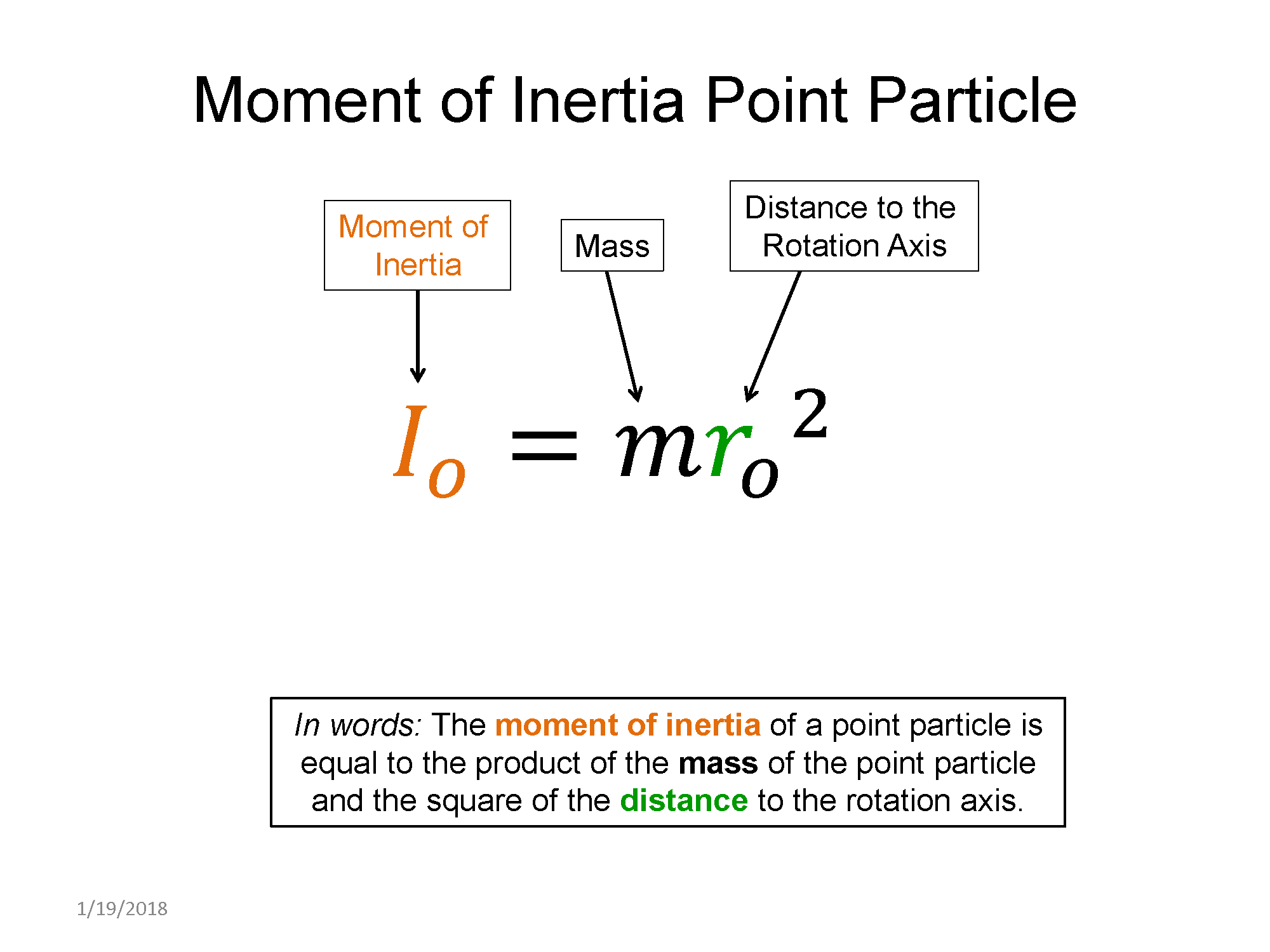
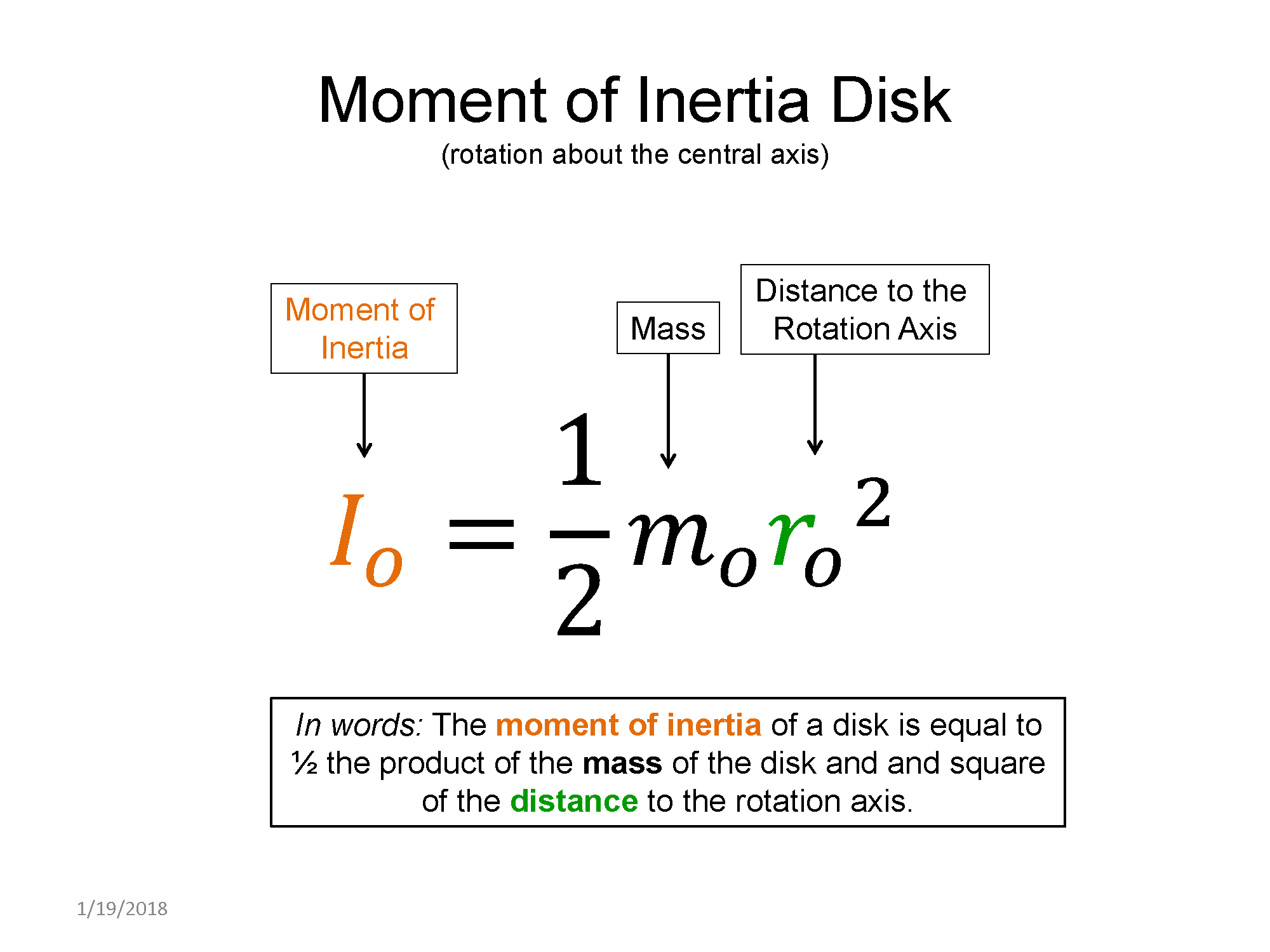
Here are some examples of moments of inertia for various mass distributions.
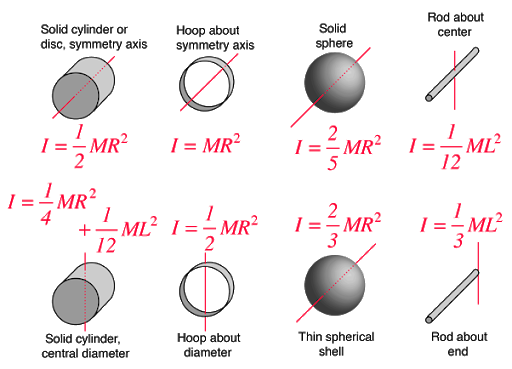
Key Equations and Infographics





Now, take a look at the pre-lecture reading and videos below.
BoxSand Videos
Required Videos
Suggested Supplemental Videos
OpenStax Reading
Fundamental examples
- set 1: Problems with solutions, Website Link
- set 2: Static net torque = 0, Website Link
- set 3: PDF of free body diagram problems, Offsite PDF Link
Post-Lecture Study Resources
Use the supplemental resources below to support your post-lecture study.
Practice Problems
Recommended example practice problems
Additional Boxsand Study Resources
Additional BoxSand Study Resources
Learning Objectives
Summary
We have previously studied Newton's laws of motion while only considering what happens to the center-of-mass (COM) of an object, otherwise known as a point particle model. In statics and dynamics, we still work under the framework of Newton's laws of motion, but we extend our consideration from the point particle model to also include the shape and size of the object. The sum of the forces on a object still determine the linear motion of it's COM, but where those forces are applied will tell us something about how and if the object rotates.
Atomistic Goals
Students will be able to...
Statics and Dynamics
1. Understand the application of Newton's laws of motion to rigid bodies, while also identifying the similarities when compared to the point particle model.
2. Demonstrate the ability to analyze a system in rotational equilibrium using the rotational version of Newton's second law.
3. Define moment of inertia.
4. Understand moment of inertia and its dependence on mass distribution. Also recognize its analogy to the previous working definition of inertia as applied to the point particle model.
5. Connect quantities found from a rotational dynamics analysis to both rotational and linear kinematics.
Stability
6. Be able to calculate the center of mass of an object or a system of objects.
7. Be able to determine if an object or system of objects will be stable based on center of mass location relative to normal forces.
YouTube Videos
Moment of inertia explanation. At 12:25 doc begins to derive moments of inertia for various objects, you can ignore this.
Doc Schuster talks about rotational dynamics.
Simulations
PhET simulation on dynamic torque. Note that when you let the wheel rotate without acceleration, it is actually in torsional equilibrium despite the fact that it is in motion.
For additional simulations on this subject, visit the simulations repository.
You need to have Java installed and updated. Download and run the file.
Demos
A demonstration of the intermediate axis theorem, an application of moment of inertia.
For additional demos involving this subject, visit the demo repository
History
Oh no, we haven't been able to write up a history overview for this topic. If you'd like to contribute, contact the director of BoxSand, KC Walsh (walshke@oregonstate.edu).
Physics Fun
Other Resources
Read pages 1-10 for static equilibrium.
This links to a set of slides detailing static equilibrium.
Resource Repository
This link will take you to the repository of other content related resources.
Problem Solving Guide
Use the Tips and Tricks below to support your post-lecture study.
Assumptions
Checklist
Misconceptions & Mistakes
Pro Tips
Multiple Representations
Multiple Representations is the concept that a physical phenomena can be expressed in different ways.
Physical
Mathematical




Graphical
Descriptive
Experimental