K-1D-1The graph shows position as a function of time for two trains running on parallel tracks.
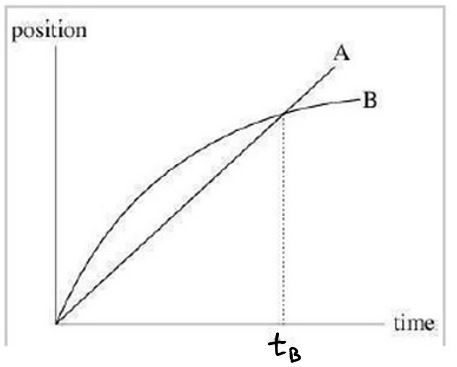
Which of the following statements are true:
1. At time tB, both trains have the same velocity.
2. Both trains speed up all the time.
3. Both trains have the same velocity at some time before tB.
4. At some instant, both trains have the same acceleration.
5. At time tB, both trains have the same magnitude of displacement from t = 0.
K-1D-2 The position of two cars as a function of time is plotted in the figure. Which of the following statements are false regarding this situation?
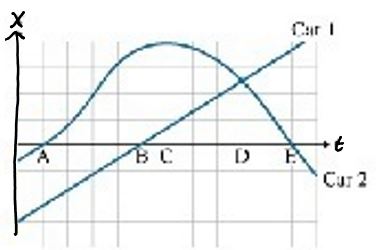
1. Car 1 has the greatest average velocity between points A and D.
2. Car 2 has the greatest average velocity between points A and D.
3. Car 2 has the same acceleration at point B as car 1 does at point E.
4. Car 2 has a greater acceleration than car 1 at point C.
5. Car 1 is momentarily at rest at point B.
6. Car 2 is momentarily at rest at point C.
K-1D-3 The velocity as a function of time for three different objects moving in a straight line are plotted to the right. Which of the following statements about their motion are necessarily (must be) true?
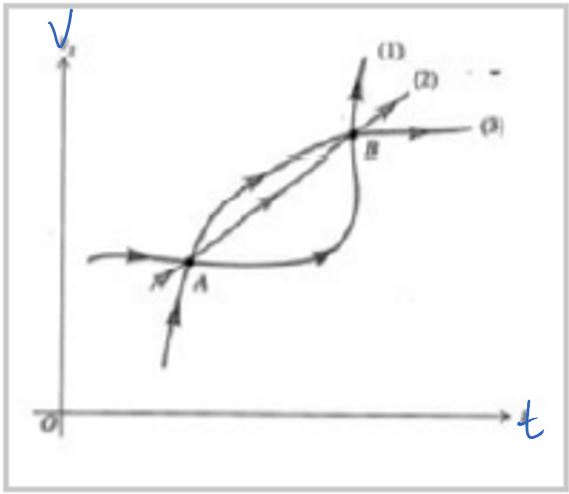
1. At point A, the position of object 3 is the same as object 1 or 2.
2. At point B, the position of object 2 is greater than object 3.
3. Halfway between time tA and tB the position of 3 is greater than 1 or 2.
4. Nothing can be determined about the position of the objects from this plot.
K-1D-4 Two balls are released from rest and undergo free-fall. Ball A is released first, followed by ball B a moment later. What happens to the distance between the balls while they are in free fall.
1. Increases
2. Decreases
3. Stays the same
K-1D-5 Can an object be increasing in speed as it’s acceleration decreases?
1. Yes
2. No
K-1D-6 Which of the following statements are false?
1. An object can be increasing in speed as it’s acceleration is decreasing.
2. An object can have zero velocity and nonzero acceleration at the same time.
3. An object can have a nonzero velocity and its acceleration be zero.
4. An object at rest can have a constant nonzero acceleration and stay stopped.
K-1D-7 Which of the following statements are false?
1. An object can be increasing in speed as it's acceleration is decreasing.
2. An object can have zero velocity and nonzero acceleration at the same time.
3. An object can have nonzero velocity and its acceleration be zero.
4. An object at rest can have a constant nonzero acceleration and stay stopped.
K-1D-8 T/F? If an object has an acceleration toward a point, then it must be getting closer and closer to that point.
K-1D-9 T/F? If an object has an acceleration toward a point, then it must be getting closer to that point?
K-1D-10 Which of the following statements are false?
1. An object can be increasing in speed as it’s acceleration is decreasing.
2. An object can have zero velocity and nonzero acceleration at the same time.
3. An object can have a nonzero velocity and its acceleration be zero.
4. An object at rest can have a constant nonzero acceleration and stay stopped.
K-1D-11 Two balls are released from rest and undergo free-fall. Ball A is released first, followed by ball B a time T0 later. The distance between the balls follows the following function of the change in time (Δt).

where g is the magnitude of the acceleration of gravity.
How does the distance change with respect to the change in time?
1. No dependence
2. Linearly
3. Quadratically
4. Cubically
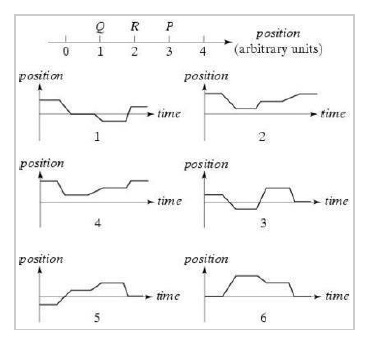
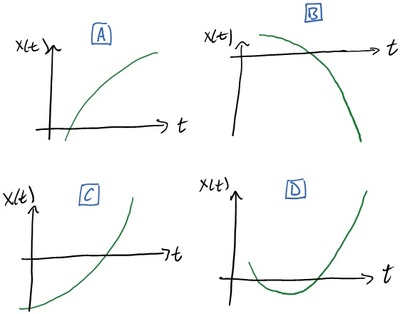
K-1D-12 A person initially at point P in the illustration stays there a moment and then moves along the axis to Q and stays there a moment. She then runs quickly to R, stays there a moment, and then strolls slowly back to P. Which of the position versus time graphs below correctly represents this motion?
K-1D-13 When is the speed maximum and the object moving in the negative direction?
.jpg)
K-1D-14 The figure shows a plot of an object's velocity as a function of time. What is the value, in m/s2, of the greatest magnitude acceleration the object undergoes.
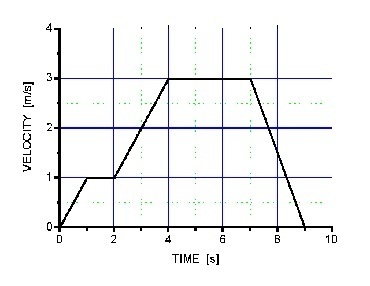
K-1D-15 Which of the following position as a function of time plots shows an object that has the direction of velocity change during the motion plotted,
shows an object that is speeding up during the entire time plotted,
shows an object that has an acceleration with a constant direction and magnitude?
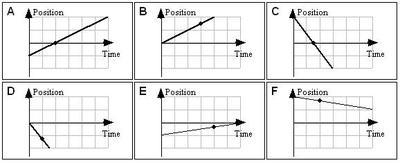
K-1D-16 The graphs below show position versus time for six boats traveling along a straight, narrow channel. The scales on both axes are the same for all of these graphs. In each graph, a point is marked with a dot. Rank the magnitude of the velocity of the boat at the point indicated.
K-1D-17 Two balls are released from rest and undergo free-fall. Ball A is released first, followed by ball B a moment later. What happens to the distance between the balls while they are in free fall.
1. Increases
2. Decreases
3. Stays the same
K-1D-18 Two runners are participating in a 5 km race. The first runner maintains a steady 5.5 kph pace while the second maintains a steady 4 kph pace. How long will the first runner wait at the finish line before the second runner arrives?
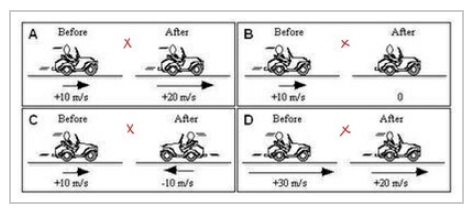
K-1D-19 In each figure below, a car's velocity is shown before and after a short time interval. Rank the magnitude of the change in velocity during the time interval.
K-1D-20 Constant Acceleration: A car traveling at 60.0 mph (26.82 m/s) suddenly slams on its brakes. If it slows at a rate of 4.60 m/s2 , how far does it travel before it comes to a complete stop? Give your answer in meters, but do not include them in your response.
K-1D-21 Can an object be increasing in speed as it’s acceleration decreases?
1. Yes
2. No
K-1D-22 The following drawings represent strobe (flash) photographs of a ball moving in the direction of the arrow. The circles represent the positions of the ball at succeeding instants of time. The time interval between successive positions is the same in all cases. Assume all accelerations are constant.
Rank the magnitude of the acceleration based on the drawings.

K-1D-23 Constant Acceleration Comparison: A sports car accelerates from zero to 30.0 mph (13.41 m/s) in 1.50 s. How many seconds does it take for it to accelerate from zero to 60.0 mph, assuming its acceleration is constant?
K-1D-24 Constant Deceleration Example: Hammy the hamster is at full sprint when all of a sudden he spots a cat in front of him. Within 0.10 s and 1 cm Hammy has uniformly reduced his speed to 0.50 cm/s, and is about to turn around and run the other way. How fast was Hammy (a) originally running when he saw the cat, and (b) what was his acceleration during this time?
K-1D-25 Comparison Example: A person standing at the edge of a cliff throws one ball straight up and another ball straight down at the same initial speed. Neglecting air resistance, which ball hits the ground below the cliff with a greater speed?
K-1D-26Two Stage Example: A construction worker’s hammer falls from rest off of the top of an apartment building. A tenant notices it takes 0.20 s for the hammer to pass their 1.6-m-tall window. How far above the top of this window is the roof?
K-1D-27 T/F? If an object has an acceleration toward a point, then it must be getting closer to that point?