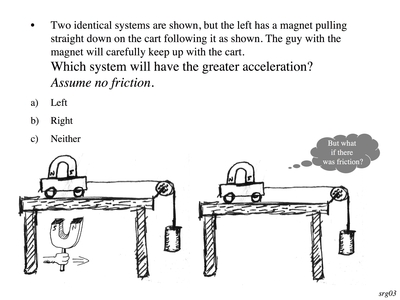
F-CS-1
F-CS-2 Which pairs of forces in the free body diagram shown could be interaction force pairs?
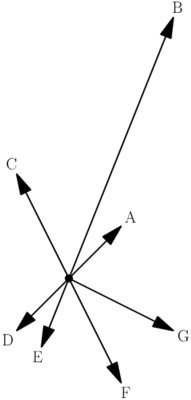
- A and D
- A and E
- B and E
- C and F
- F and G
- None of these
F-CS-3 The diagram shows two blocks (on a frictionless horizontal surface) with two external forces acting, one on each block as shown.
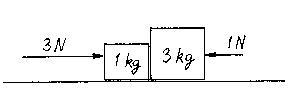
Compared to the net force on the smaller block, the net force on the larger block is _____
- equal in magnitude & opposite in direction.
- equal in magnitude & in the same direction.
- larger in magnitude & opposite in direction.
- larger in magnitude & in the same direction.
- smaller in magnitude & opposite in direction.
- smaller in magnitude & in the same direction.
- zero, since both net forces vanish & have no direction.
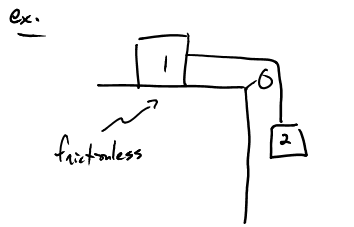
F-CS-4 A box is on a horizontal frictionless table and is attached via a string and pulley to a another mass M that is hanging off the end of the table.
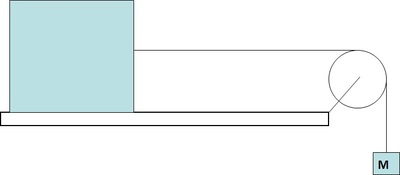
The tension in the cable is ___________
greater than Mg
less than Mg
equal to Mg
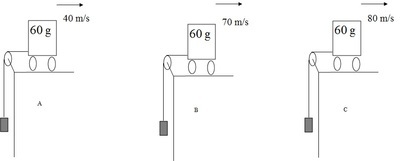
F-CS-5 Rank the following situations, greatest to least, based on the tension in the string. Assume the hanging mass in each case is the same, friction is negligible, and the pulley and the rope are massless.
Which of the following are constraints on mass 1 and mass 2?

- |a1|= |a2|
- |a1|= 2 |a2|
- |v1|= |v2|
- |v1|= 2 |v2|
F-CS-6 The figure shows the use of a pulley to obtain mechanical advantage when lifting an object. Mechanical advantage is defined as the ratio of the force required to do a task without the use of a device divided by the force required with the device. What is the mechanical advantage of the pulley system shown in the figure.

The box of mass m is suspended above the floor of an elevator with the aid of some mass-less, friction-less pulleys. The elevator is moving in the upward direction and slowing down.

Which of the of the following are true regarding the tension in the cable?
- greater than mg
- equal to mg
- greater than mg/2 and less than mg
- equal to mg/2
- greater than mg/4 and less than mg/2
- equal to mg/4
- less than mg/4