E-PE-1a Starting from rest, two identical 2-kg masses slide down different angle frictionless inclines.
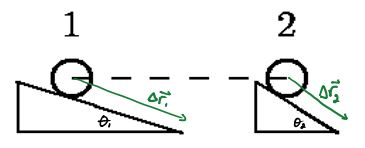
If the angle from the horizontal in the second case is 65o and the incline is 11.03 m long, how fast will the mass be moving when it reaches the bottom of the incline?
E-PE-1b Starting from rest, the same two identical 2-kg masses slide down different angle inclines that both have identical coefficients of kinetic friction.
Which mass will have the greater final kinetic energy when reaching the bottom.
1. 1
2. 2
3. same
4. not enough information
E-PE-2 A 2-kg mass is compressed 1 m against a spring whose spring constant k is 20 N/m. Once released the mass slides down a frictionless ramp then back up to another spring with the same spring constant. After compressing the second spring it comes to rest and is held in place. Rank the work done by the normal force from the ground during the following intervals.
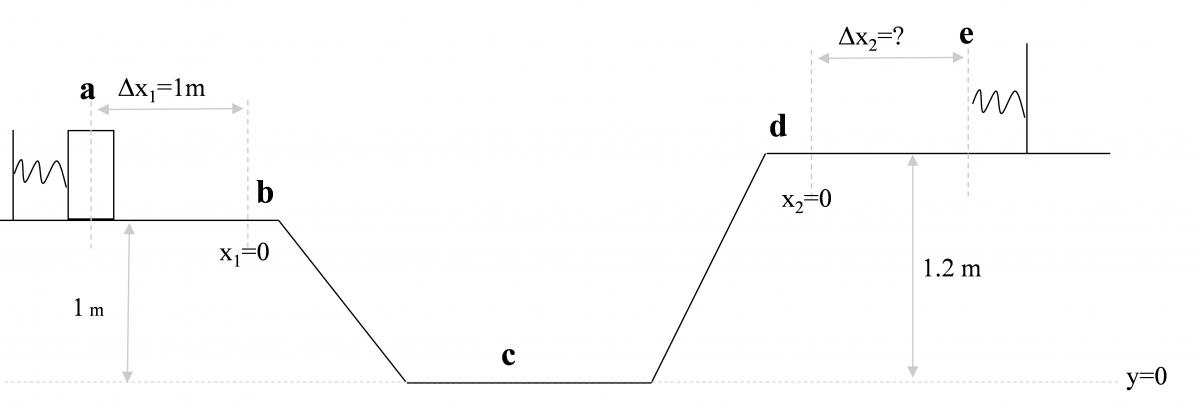
• a to b
• b to c
• c to d
• d to e
What is the speed in m/s of the mass at point c?
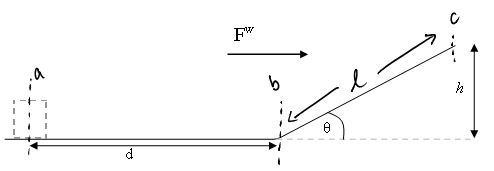
E-PE-3 A box of mass m starts from rest on a horizontal surface on a planet with an acceleration of gravity g. Wind applies a constant horizontal force Fw on the box. After traveling a distance d on the horizontal surface the box encounters an inclined plane that makes an angle of θ up from the horizontal. To what height h will the box reach before momentarily coming to rest? All surfaces are frictionless.
E-PE-4 A 50-kg person stands on a 25-kg platform. He pulls on the rope that is attached to the platform via the frictionless pulley system shown here. If he pulls the platform up at a steady rate, and pulls the rope through a distance of 2 meters, how much work does the rope do on the man? Ignore friction and assume g = 10 m/s2.
