Note to user: The numbering system used, E-WKE refers to Energy, E, as the main topic and Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem, WKE, as the subtopic.
E-WKE-1 Two marbles, one twice as heavy as the other, are dropped to the ground from the roof of a building. Just before hitting the ground, the heavier marble has
a. as much kinetic energy as the lighter one.
b. twice as much kinetic energy as the lighter one.
c. half as much kinetic energy as the lighter one.
d. four times as much kinetic energy as the lighter one.
e. impossible to determine
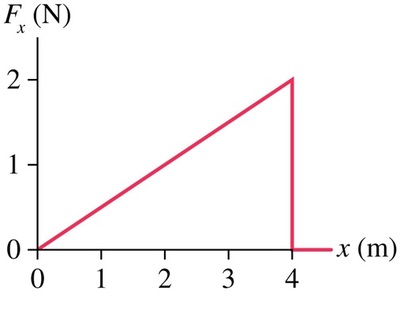
E-WKE-2 A particle moving along the x-axis experiences the force shown in the graph. If the particle has 2.0 J of kinetic energy as it passes x = 0 m, what is its kinetic energy when it reaches x = 4 m?
E-WKE-3 Which force does the most work?

E-WKE-4 A crane raises a steel girder into place at a construction site. The girder moves with constant speed. Consider the work Wg done by gravity and the work WT done by the tension in the cable. Which of the following is correct?
a. Wg and WT are both zero.
b. Wg is negative and WT is negative.
c. Wg is negative and WT is positive.
d. Wg is positive and WT is positive.
e. Wg is positive and WT is negative.
E-WKE-5 A crane raises a steel girder into place at a construction site. The girder is moving downward and slowing down. Which of the following statements about the girder are true.
a. The kinetic energy is increasing
b. The kinetic energy is decreasing
c. The work from the cable is positive
d. The work from the cable is negative
e. The work from gravity is positive
f. The work from gravity is negative
g. The magnitude of the work from the cable is greater than that from gravity
h. The magnitude of the work from the cable is less than that from gravity
i. The magnitude of the work from the cable is equal to that from gravity
E-WKE-6a A 2-kg-block, initially at rest, is being pulled horizontally by a 5-N tension force. The coefficient of static and kinetic friction between the block and the surface is 0.5 and 0.2, respectively. What are the sign of the following quantities?
A. Work from gravity
B. Work from the normal force
C. Work from the tension
D. Work from the friction
E-WKE-6b Now sliding in direction of tension, what are the signs of the following quantities?
A. Work from gravity
B. Work from the normal force
C. Work from the tension
D. Work from the friction
E-WKE-7 A cart on an air track is moving at 0.5 m/s when the air is suddenly turned off. The cart comes to rest after traveling 1 m. The experiment is repeated, but now the cart is moving at 1 m/s when the air is turned off. How far does the cart travel before coming to rest?
E-WKE-8 A pendulum bob swings in a complete vertical circle. At what point does the tension in the string do the most work?
a. Bottom of the loop
b. Top of the loop
c. The tension does no work
E-WKE-9a Two people are on low friction carts, throwing a medicine ball back and forth, speeding up the rate at which they move away from each other.
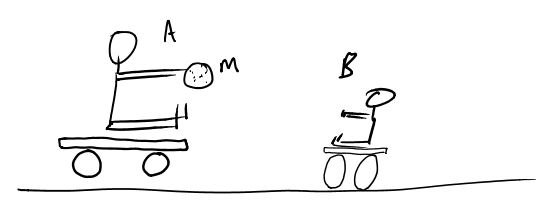
What is the sign of the work of the ball on person A while they catch the ball?
a. positive
b. negative
c. zero
E-WKE-9b What is the sign of the work of the ball on person A while they throw the ball?
a. positive
b. negative
c. zero
E-WKE-10a The diagram depicts two pucks on a frictionless table. Puck II is four times as massive as puck I. Starting from rest, the pucks are pushed across the table by two equal forces. The forces are active all the way to the finish line.
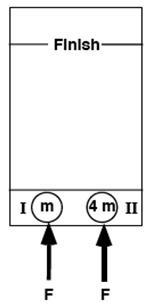
E-WKE-10b Which puck will have the greater kinetic energy upon reaching the finish line?
a. Puck I
b. Puck II
c. Both will have the same.
d. There is not enough information to decide.
E-WKE-11 The diagram depicts two pucks on a frictionless table. Puck II is four times as massive as puck I. Starting from rest, the pucks are pushed across the table by two equal forces. The forces act on both of them for 6.0 s.
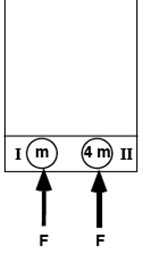
Rank the final kinetic energy of the two pucks.
E-WKE-12 A stuntman is sliding toward a brick wall with wind blowing down and against their motion. Strapped to their back is a rocket providing thrust.
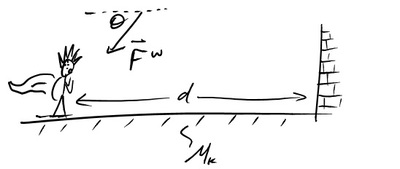
What is the sign of the work for each force acting on the stuntman?
E-WKE-13 A truck is accelerating with a box in the bed of the truck.

What is the sign of the following work?
A. friction from road on truck
B. friction from the truck on the box
C. normal force from the truck on the box
D. friction from the box on the truck
E. normal force from the box on the truck
E-WKE-14 A gondola with a box inside is accelerating up and at an angle from the horizontal.
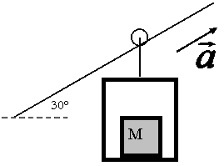
What is the sign of the following work?
A. gravity on box
B. gravity on gondola
C. normal force on box
D. normal force on gondola
E. friction on box
F. friction on gondola
G. tension from cable on box
E-WKE-15 Starting from rest, two identical 2-kg masses slide down different angle frictionless inclines.
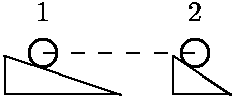
If the angle from the horizontal in the first case is 30o and the incline is 20.0 m long, how much work does gravity do on the first mass while sliding down the incline?
E-WKE-16 Three students are discussing the concept of work in regards to a situation where a dude is standing at rest holding some books. Which student do you agree with most?
1. “The books aren't moving so there is no way any work is being done on them.”
2. “That doesn't make sense because the dudes arms would be getting tired and thus he must be losing energy, if energy is being lost then work must be done on the dude”
3. “The only force connecting the books and that dude are the normal force, so if the books have no work being done on them but the dude does have work being done on him it can’t be due to the normal force from the books.”
4. All are correct statements
E-WKE-17 A 50-kg person stands on a 25-kg platform. He pulls on the rope that is attached to the platform via the frictionless pulley system shown here. If he pulls the platform up at a steady rate, and pulls the rope through a distance of 2 meters, how much work does the rope do on the man? Ignore friction and assume g = 10 m/s2.
