BoxSand's Resources
Introduction
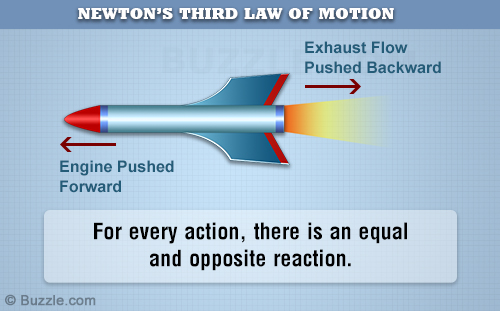
Newton's Third Law says that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. This means that if I push on the wall with 30N of force, the wall must push back on me, in the exact opposite direction, with exactly 30N. We call these two forces Force Pairs. We identify force pairs with a Free-body Diagram, which is one of the most important tools for solving many force problems.
Videos
Pre-lecture videos
Newton's Laws (6 min)
https://media.oregonstate.edu/media/t/0_ta9bhwiy
Free Body Diagrams and 3rd Law Force Pairs (14 min)
https://media.oregonstate.edu/media/t/0_fw6g0y3q
Web Resources
Text
The physics classroom introduces Newton's third law:
How to identify action and reaction force pairs:
Here is a concise definition of Newton's Third Law;
This a comprehensive introduction to Newton's third law. This online textbook discusses Newton's third law with diagrams, worked problem examples, and interactive conceptual questions. All notation in this text is consistent with BoxSand's.
Other Resources
This link will take you to the repository of other content related resources.
Videos
Khan Academy's introduction to Newton's Third Law in a 2 part video sequence:
Doc Schuster introduces Newton's Third Law with a great visual to help understand action/reaction pairs:
Other Resources
This link will take you to the repository of other content related resources.
Simulations
This first interactive game will challenge you with a few questions after a bout of Third Law tug-of-war with a cart;
This next simulation shows how every force pair is always equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. Make sure to check the "Force" box to see a pictorial representation of the forces.
For additional simulations on this subject, visit the simulations repository.
Demos
Action-reaction push me pull me carts,
For additional demos involving this subject, visit the demo repository
Practice
Fundamental examples
1. Two astronauts, Susan and Kelly are in outer space. Susan pushes off of Kelly with a force, $\vec{F}=\langle14,0,0\rangle$. What is the force that Kelly pushes on Susan with?
a) $\vec{F}=\langle14,0,0\rangle$
b) $\vec{F}=\langle 0,0,14 \rangle$
c) $\vec{F}=\langle-14,0,0\rangle$
d) not enough information given
2. In the image below, box 1 sits on top of a table at rest. Box 2 sits on top of box 1 and is at rest with respect to box 1. The system is in equilibrium. Identify the 3rd law force pairs.
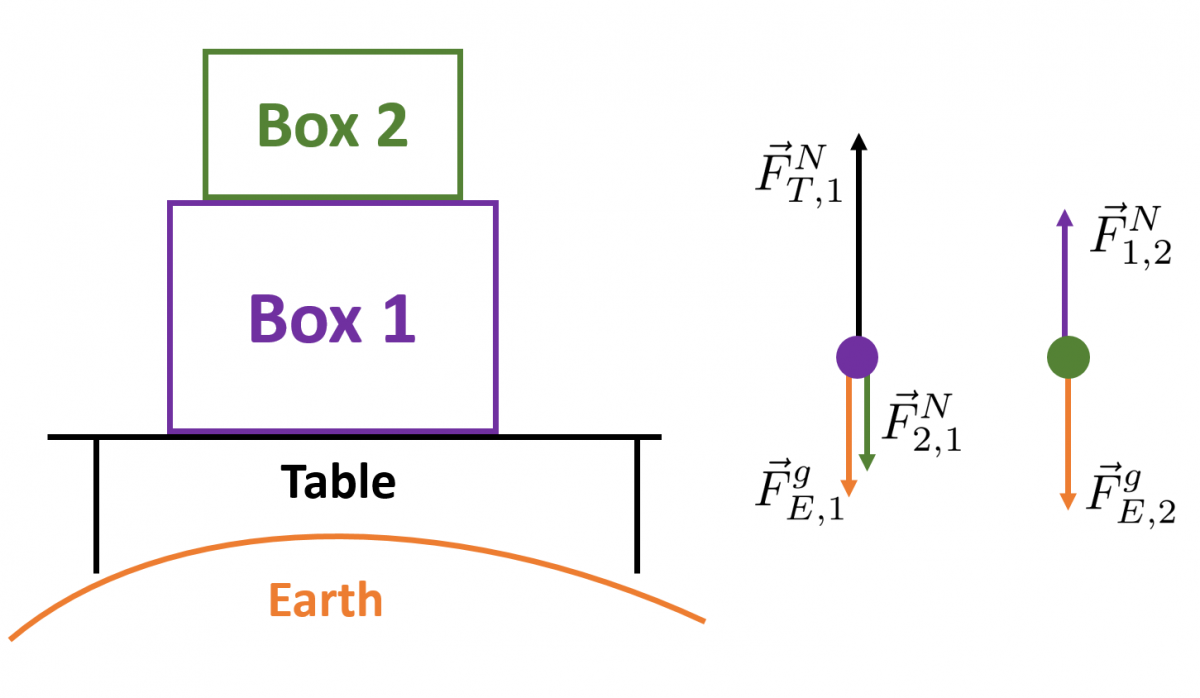
a) $\vec{F}^{g}_{1}$ & $\vec{F}^{g}_{2}$
b) $\vec{F}^{g}_{1}$ & $\vec{F}^{N}_{1,2}$
c) $\vec{F}^{g}_{2}$ & $\vec{F}^{N}_{1,2}$
d) $\vec{F}^{N}_{2,1}$ & $\vec{F}^{N}_{1,2}$
3. Box 3 sits on top of Box 2 which sits on top of Box 1. Identify all of the 3rd law force pairs.
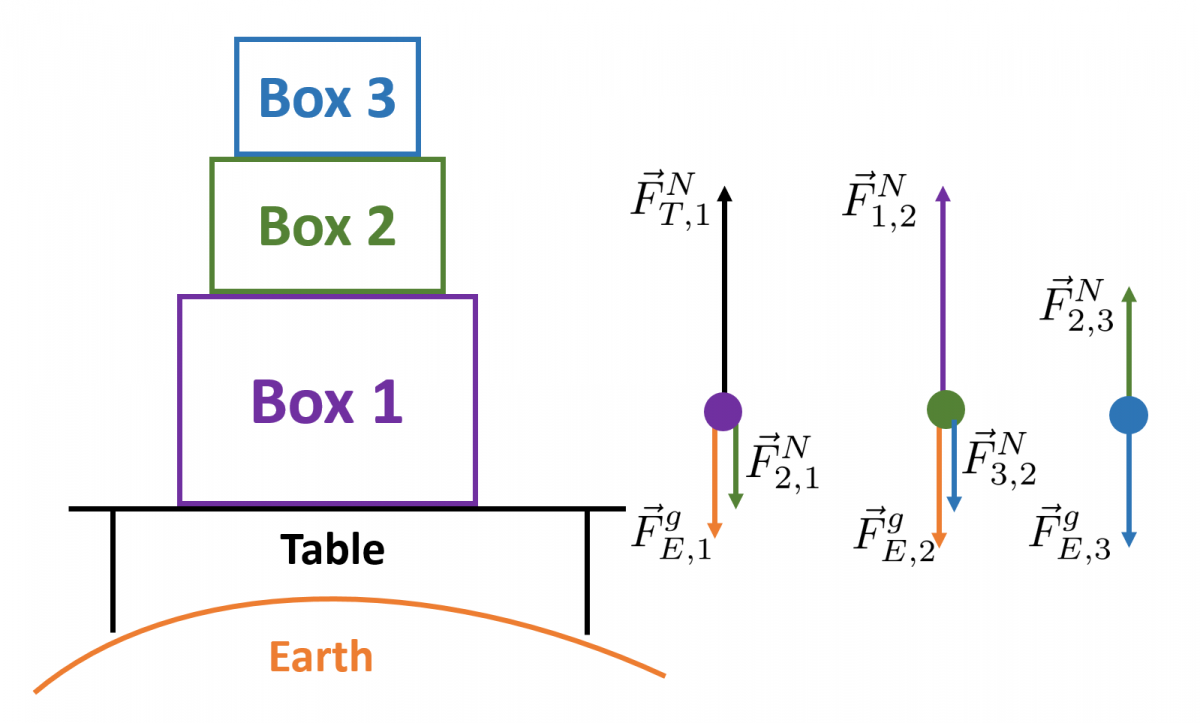
a) $\vec{F}^{N}_{2,3}$ & $\vec{F}^{N}_{1,2}$
b) $\vec{F}^{N}_{2,1}$ & $\vec{F}^{N}_{1,2}$
c) $\vec{F}^{N}_{2,3}$ & $\vec{F}^{N}_{2,1}$
d) $\vec{F}^{N}_{2,3}$ & $\vec{F}^{N}_{3,2}$
e) $\vec{F}^{N}_{2,1}$ & $\vec{F}^{N}_{2,3}$
CLICK HERE for solutions.
Short foundation building questions, often used as clicker questions, can be found in the clicker questions repository for this subject.
Practice Problems
Worked Examples
Recommended example practice problems
BoxSand's Quantitative Practice Problems
BoxSand's Multiple Select Problems
Set 1: Physics lab, 3rd law forces vs 2nd law forces WORKSHEET
Set 2: Identifying action and reaction force pairs
Set 3: The Physics Classroom Newton's Third Law problems
For additional practice problems and worked examples, visit the link below. If you've found example problems that you've used please help us out and submit them to the student contributed content section.